- Title
-
Thrombospondin-4 controls matrix assembly during development and repair of myotendinous junctions
- Authors
- Subramanian, A., Schilling, T.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
Zebrafish Tsp4b localizes to all muscle attachments.(A-L) Whole mount immunostaining of wild type embryos using anti-MHC (A, D, G, J; green) and anti-Tsp4b (B, E, H, K; red) and merged (C, F, I, L). (A-C) 20-22 hpf and (D-F) 72 hpf (lateral view) trunk showing early Tsp4b localization around notochord and medial somite boundaries (B and C) and later at somite boundaries (E and F). (G-L) Ventral (G-I) and lateral (J-L) views of 72 hpf showing Tsp4b at cranial muscle attachments. Abbreviations: AM-Adductor Mandibularis, AH-Adductor Hyoideus, AO-Adductor Operculae, DO-Dilator Operculae, HH-HyoHyal, IH-InterHyal, IMA-InterMandibularis Anterior, IMP-InterMandibularis Posterior, IO-Inferior Oblique, IR-Inferior Rectus, LAP-LevatorArcus Palatini, MR-Medial Rectus, SH-SternoHyoideus. Scale bar = 30 microns. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Tsp4b is required for muscle attachment.Whole mount immunostaining of 36 hpf Tsp4b-deficient embryos using anti-MHC (A, D, G; green) and anti-Tsp4b (B, E, H; red) and merged (C, F, I). (A-C) Injection of 0.32 ng tsp4b-MO eliminates Tsp4b protein at 72 hpf but myofibers attach. (D-F) Electrical stimulation (30 V) of these larvae causes muscle detachment. (G-I) Co-injection of tsp4b RNA (80 pg/embryo) rescues muscle attachment and Tsp4b localization. (J) Histogram showing muscle detachment in 76% (N = 79) of stimulated Tsp4b-deficient embryos (Chi squared test p-value<0.001). (K) Co-injection of tsp4b mRNA rescues muscle attachment in 67% (N = 92) of stimulated Tsp4b-deficient embryos (Chi squared test p-value<0.001). (p-value representation legend: significant *<0.05, highly significant **<0.01, extremely significant ***<0.001, extremely significant ****<0.0001). Scale bar = 30 microns. |
|
Tsp4b has a non cell-autonomous function in muscle attachments.(A-L) 48 hpf (lateral views) of genetic mosaics generated by cell transplantation. GFP-labeled wild type muscle cells (green) (A and I) or putative tenocytes (arrow heads) (green) (E) were grafted into Tsp4b-deficient host embryos and stained with anti-Tsp4b (B, F, J; red), and anti-MHC (C, G, K; gray/white). (I-L) Transplants locally rescued muscle detachment after stimulation in regions where Tsp4b was restored (white line denotes region lacking Tsp4b). Scale bars = 30 microns. |
|
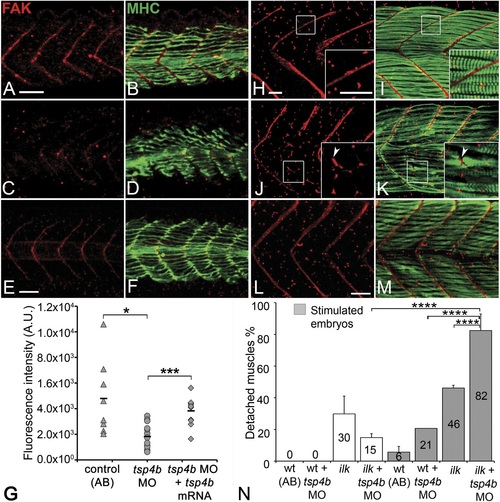
(A-F) Lateral views of 20-24 hpf embryos stained with anti-phosphorylated (Tyrosine 861) FAK (pFAK; red) and anti-MHC (green). (A and B) pFAK localizes to the ends of early myofibers at wild-type somite boundaries. (C and D) Reduced pFAK levels in Tsp4b-deficient embryos. (E and F) pFAK levels are restored in Tsp4b-deficient embryos injected with full length tsp4b mRNA. (G) Fluorescence intensity measurements (arbitrary units [A.U.]) for pFAK staining along somite boundaries confirm significant reductions in Tsp4b-deficient embryos, and partial rescue by co-injection of full length tsp4b mRNA (t test: one tailed, unequal variance; p-value: wt and tsp4b-deficient <0.05; Tsp4b-deficient and Tsp4b-deficient + tsp4b RNA p<0.001). (H-M) 36 hpf (lateral views) stained with anti-pFAK (red), and anti-MHC (green). Insets show higher magnification images of white boxed areas. (H and I) pFAK localizes to muscle sarcolemma. (J and K) In Tsp4b-deficient embryos, pFAK is reduced/discontinuous at somite boundaries. pFAK associates with ectopic muscle attachments (arrowheads). (L and M) pFAK localization is restored in Tsp4b-deficient embryos injected with full length tsp4b mRNA. (N) Embryo percentages (N = 70 embryos) with detached muscles from an intercross between two ilk+/- heterozygotes, injected with sub-threshold amounts (0.16 ng) of tsp4b-MO and stimulated (30 V) (Chi squared test; p-value: wt+ tsp4b-MO (stimulated) and ilk+tsp4b-MO (stimulated) p<0.0001, ilk (stimulated) and ilk+tsp4b-MO (stimulated) p<0.0001, ilk+ tsp4b-MO and ilk+tsp4b-MO (stimulated) p<0.0001). Scale bar = 30 microns. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
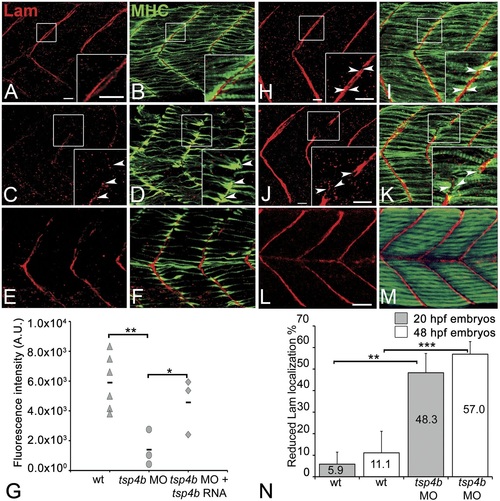
Tsp4b is required for Laminin assembly at MTJs.(A-F) Lateral views of somites in 20 hpf embryos stained with anti-MHC (green) and anti-pan-Laminin (Lam, red) antibodies. Insets show higher magnification images of the areas marked by white boxes, where Lam localizes to developing myotendinous ECM (arrowheads). (A and B) Wild-type siblings. (C and D) tsp4b-MO injected embryos showing local loss of Lam at 20 hpf, and ectopic muscle attachments (arrowheads) at remaining Lam foci. (E and F) Lam localization was restored in Tsp4b-deficient embryos injected with full length tsp4b mRNA. (G) Fluorescence intensity measurements (arbitrary units [A.U.]) at somite boundaries of anti-Lam in 20-24 hpf wild type controls versus embryos injected with tsp4b-MO or co-injected with tsp4b-MO and tsp4b RNA. (t test: one tailed, unequal variance; p-value: wt and Tsp4b-deficient <0.01, Tsp4b-deficient and Tsp4b-deficient and tsp4b RNA <0.05) Scale bar = 30 microns. (H and I) Lateral views of somites in wild type embryos at 36 hpf stained with anti-pan-Lam (red), and anti-MHC (green). Insets show higher magnification images of white boxed areas. Lam localizes to myotendinous ECM (I, arrowheads). (J and K) In Tsp4b-deficient embryos, Lam is reduced/discontinuous at somite boundaries (K, arrowheads). (L and M) Lam localization is restored in Tsp4b-deficient embryos injected with full length tsp4b mRNA. (N) Embryo percentages (20 hpf embryos N = 30, 72 hpf embryos N = 50) with reduced/mislocalized Lam at 20 and 48 hpf in wild type and Tsp4b-deficient embryos. (Chi squared test; p-values: 20 hpf **<0.01, 48 hpf ***<0.001) Scale bar = 30 microns. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
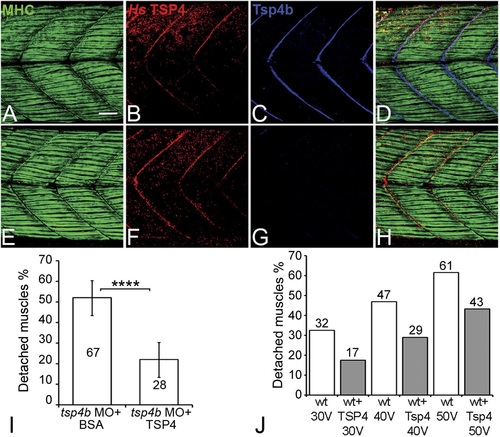
Conserved functions for TSP4 in maintenance of MTJs. (A-H) Lateral views of trunk muscles in 72 hpf embryos stained with anti-MHC (green), anti-human TSP4 (red) and anti-Tsp4b (blue) antibodies. (A-D) Injected recombinant human TSP4 co-localizes with zebrafish Tsp4b at muscle attachments in wild type embryos. (E-H) Injected TSP4 localizes to somite boundaries in Tsp4b-deficient embryos. (I) Injected TSP4 rescues muscle attachments in Tsp4b-deficient embryos upon stimulation (N = 96 embryos) (Chi squared test, p value<0.001). (J) Histogram showing percentage of embryos with detached muscles in 60 hpf wt+BSA (white columns) and wt+TSP4 (shaded columns) embryos, stimulated at 30 V, 40 V and 50 V, respectively. N = 40 embryos for each sample. (Scale bars = 30 microns). |