- Title
-
Different combinations of Notch ligands and receptors regulate V2 interneuron progenitor proliferation and V2a/V2b cell fate determination
- Authors
- Okigawa, S., Mizoguchi, T., Okano, M., Tanaka, H., Isoda, M., Jiang, Y.J., Suster, M., Higashijima, S.I., Kawakami, K., Itoh, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
Mib-mediated Notch signaling regulates both p2 progenitor maintenance and the V2a/V2b cell fates. (A, B) p2 progenitors in the ventricular zone were reduced in mib mutants. irx3a (A) or nkx6.1 (B) Expression in sibling control (sib) or mib mutants (mib). Increased ventral irx3a-expressing cells in mib mutants are primary motoneurons. (C, D) V2a was increased and expanded into the ventricular zone due to precocious differentiation and V2b was reduced in mib mutants. V2a and V2b cells were detected by vsx2 (C) and sclα (D), respectively in sibling control (sib) or mib mutants (mib). Left two panels: side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Dorsal and ventral borders of the neural tubes are shown by the dotted lines. Bar scale: 100 Ám. Right two panels: transverse sections through the trunk region in embryos at 24 hpf. p2 Progenitor domains within the neural tubes (circled by white dotted lines) are indicated by red dashed outlines. Bar scale: 20 Ám. |
|
DeltaA and DeltaD are redundant for p2 progenitor maintenance. (A, B) p2 progenitors were significantly reduced in deltaA/D double mutant embryos compared with any single or other double mutants. p2 Progenitors were detected by irx3a (A) or nkx6.1 (B). Sibling control (sib), deltaA mutant (dladmc72a), deltaD mutant (dldtr33), deltaA/D double mutants (dladmc72a; dldtr33), control morpholino injected embryo (con MO), deltaC morpholino injected embryo (dlc MO), deltaA/deltaC double morpholino injected embryo (dla; dlc MO), or deltaC/deltaD double morpholino injected embryo (dlc; dld MO). Left four panels in each row: side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Dorsal and ventral borders of the neural tubes are shown by the dotted lines. Bar scale: 100 Ám. Right two panels: transverse sections through the trunk region in embryos at 24 hpf. p2 Progenitor domains within the neural tubes (circled by white dotted lines) are indicated by red dashed outlines. Bar scale: 20 Ám. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Mib, DeltaA, DeltaC, and DeltaD, but not Delta4 play important roles in V2 development. (A?E) V2a and V2b cells were identified as vsx1:GFP/Vsx2 double positive and vsx1:GFP/Scl double positive cells, respectively. Side views of embryos (control MO, deltaA/deltaC double MOs, deltaA/deltaD double MOs, deltaA/deltaC/deltaD triple MOs, or mib MO) at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Bar scale: 50 Ám. (F) V2a and V2b cell numbers per section, (G) total V2 cell number (V2a+V2b) per section, and (H) V2a-to-V2b ratio in mib and delta knockdown embryos. (F?H) Control MO, n=21; mib MO, n=4; deltaA MO, n=23; deltaC MO, n=4; deltaA MO, n=5; delta4/deltaA MOs, n=25; delta4/deltaC MOs, n=14; deltaA/deltaC MOs, n=27; deltaA/deltaD MOs, n=20; deltaA/deltaC/deltaD MOs, n=8. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences relative to the control (p<0.01). Error bars, SEM. |
|
Notch1a, Notch1b, and Notch3 together contribute to p2 progenitor maintenance. p2 Progenitors in the ventricular zone detected by irx3a (A) or nkx6.1 (B) were reduced in notch1a/notch1b/notch3 knockdown embryos (90%, irx3a, n=10; 80%, nkx6.1, n=10). Other single or double knockdown embryos did not show a striking reduction in irx3a (A) or nkx6.1 (B) expression compared with the notch1a/notch1b/notch3 knockdown embryos. All panels: side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Dorsal and ventral borders of the neural tubes are shown by the dotted lines. Bar scale: 100 Ám. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Notch1a is mainly required for the V2a/b fate decision, and Notch1a, Notch1b, and Notch3 are redundant for p2 progenitor cell maintenance. (A?G) Increased V2a and decreased V2b cell numbers were seen in notch1a, notch1a/notch1b, notch1a/notch3, and notch1a/notch1b/notch3, but not in notch1b, notch3, or notch1b/notch3 knockdown embryos. V2a and V2b cells were identified as vsx1:GFP/Vsx2 double positive- and vsx1:GFP/Scl double positive-cells, respectively. (A?E) side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Bar scale: 50 Ám. (F) V2a and V2b cell numbers per section. (G) Total V2 cell numbers (V2a+V2b) per section in notch knockdown embryos. (H) V2a-to-V2b ratio in notch knockdown embryos. (F?H) Control MO, n=21; notch1a MO, n=16; notch1b MO, n=9; notch3 MO, n=8; notch1a/notch1b MOs, n=19; notch1a/notch3 MOs, n=7; notch1b/notch3 MOs, n=12; notch1a/notch1b/notch3 MOs, n=14. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences relative to the control (p<0.005). Error bars, SEM. |
|
p2 Progenitor maintenance and V2 fate determination occur concurrently. (A) V2a and V2b cell numbers per section, (B) total V2 cell numbers (V2a+V2b) per section, and (C) V2a-to-V2b ratios, in embryos treated with DBZ either from 11 to 17 hpf (DBZ 11-17 h) or from 17 to 28 hpf (DBZ 17-28 h). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences relative to the control (p<0.01). Error bars, SEM. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Knockdown/mutation of Delta family members affects V2 interneuron development. (A, E) DeltaA and DeltaD are redundant for p2 progenitor maintenance. Both V2a and V2b cells were increased and expanded into the ventricular zone in deltaA/D double mutants. Control (sib), deltaA mutant (dladmc72a), deltaD mutant (dldtr33), deltaA/D double mutants (dladmc72a; dldtr33). (B, C, F, and G) DeltaA and DeltaC are redundant for V2a/V2b cell fate determination. V2a cell numbers were increased, whereas V2b cell numbers were not dramatically changed, and their localization was altered to the ventricular zone in deltaA/C double knockdown embryos. (C, G) Mutation in deltaC combined with deltaA knockdown led to increased V2a cell numbers and comparable V2b cell numbers (100%, vsx2, n=21; 100%, sclα, n=22). (D, H) DeltaC and DeltaD are redundant for p2 progenitor maintenance. Mutation in deltaC combined with deltaD knockdown resulted in increased V2a and V2b cell numbers (100%, vsx2, n=8; 100%, sclα, n=7). Homozygous deltaCtit446 mutant embryos were injected with control or deltaA MO (C, G) or with deltaD MO (D, H). V2a and V2b cells were detected by vsx2 (A?D) and sclα (E?H), respectively. Left four panels (in A?H): side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Dorsal and ventral borders of the neural tubes are shown by the dotted lines. Bar scale: 50 Ám. Right two panels (in A, B, E, and F): transverse sections through the trunk region in embryos at 24 hpf. The neural tubes are circled by white dotted lines. Bar scale: 20 Ám. |
|
The trap line DMC72a harbors a gene trap insertion in the deltaA locus. (A) The trap vector was inserted into exon 1 of the deltaA gene. (B) The primers dla-544F, delATG13R, and hsp70-33R were used for genotyping. (C) The insertion interferes with deltaA translation. DeltaA protein was not detected in embryos homozygous for the deltaAdmc72a allele. |
|
DeltaA but not DeltaC knockdown slightly increases both V2a and V2b cells. (A?E) V2a and V2b cells were identified as vsx1:GFP/Vsx2 double positive and vsx1:GFP/Scl double positive cells, respectively. Side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Bar scale: 50 Ám. |
|
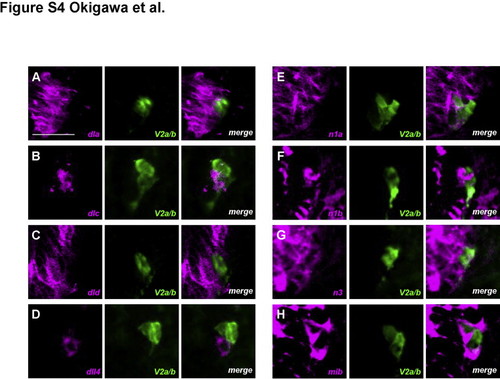
Expression patterns of Notch ligands and receptors in and around V2 neuronal lineage cells. deltaA, deltaD, notch1a, notch1b, notch3, and mib mRNAs were detected in the spinal cord and in and around V2 neurons, visualized with an anti-GFP antibody (A, C, E, F, G, and H). In contrast, deltaC was expressed in one of a pair of V2 neurons, which was likely to be a V2a cell (B). dll4 was detected not in but adjacent to V2 neurons (D). Transverse sections through the trunk region in embryos at 24 hpf. All images are of the right lower portion of the neural tube. mRNAs were mainly in the cytoplasm, whereas GFP was in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Bar scale: 20 Ám. |
|
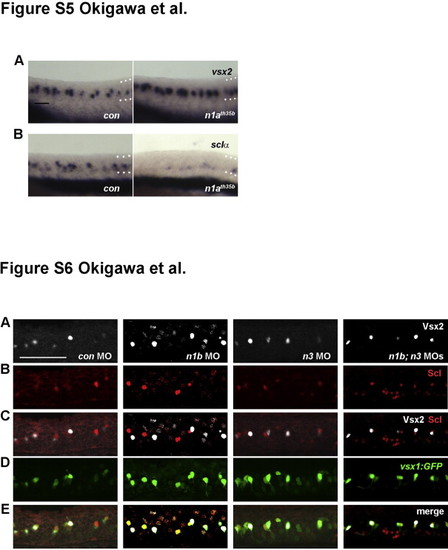
Notch1a is required for the V2a/V2b cell fate determination. (A, B) V2a cell numbers were increased, whereas V2b cell numbers were slightly reduced in notch1ath35b mutant embryos. V2a and V2b cells were detected by vsx2 (A) and sclα (B), respectively (75%, vsx2, n=12; 100%, sclα, n=11). All panels: side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Dorsal and ventral borders of the neural tubes are shown by the dotted lines. Bar scale: 50 Ám. Fig. S6: Effects of compound and single knockdown of Notch1b and Notch3 on V2 interneuron development. (A-E) V2a and V2b cells were identified as vsx1:GFP/Vsx2 double positive and vsx1:GFP/Scl double positive cells, respectively. Side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Bar scale: 50 Ám. |
|
DBZ-treatment affects V2 interneuron development. (A?E) V2a and V2b cells were identified as vsx1:GFP/Vsx2 double positive and vsx1:GFP/Scl double positive cells, respectively. Embryos were treated with DBZ either from 11 to 17 hpf (DBZ 11?17) or from 17 to 28 hpf (DBZ 17?28). Side views of embryos at 24 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Bar scale: 50 Ám. Fig. S8: Reduction of p2 progenitor cells by17-28 hpf DBZ treatment. p2 progenitor cells detected by irx3a (C) and nkx6.1 (D) in embryos treated with DBZ at 17?28 hpf were slightly but significantly reduced compared to those treated at 11?17 hpf (irx3a (A) and nkx6.1 (B)) (70%, irx3a, n=10; 80%, nkx6.1, n=10). Left two panels: side views of embryos at 28 hpf with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Dorsal and ventral borders of the neural tubes are shown by the dotted lines. Bar scale: 50 Ám. Right two panels (in C, D): transverse sections through the trunk region in embryos at 28 hpf. p2 Progenitor domains within the neural tubes (circled by white dotted lines) are indicated by red dashed outlines. Bar scale: 20 Ám. |
|
Expression patterns of her9 and hes6 in and around V2 neuronal lineage cells. her9 mRNA Expression was detected in the spinal cord but not within V2 neurons in control embryos (A). In contrast, slightly higher hes6 mRNA expression was observed in one of a pair of V2 neurons (B). In deltaA/deltaD double MO-injected embryos, some but not all of the GFP-positive V2 cells (V2a or V2b) expressed hes6 (C). In notch1a knockdown embryos, GFP-positive V2 cells (most of which were V2a and not V2b) expressed her6 very weakly (D). Transverse sections through the trunk region in embryos at 24 hpf. All images are of the right lower portion of the neural tube. The mRNAs were mainly in the cytoplasm, whereas GFP was in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Bar: 20 Ám. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 391(2), Okigawa, S., Mizoguchi, T., Okano, M., Tanaka, H., Isoda, M., Jiang, Y.J., Suster, M., Higashijima, S.I., Kawakami, K., Itoh, M., Different combinations of Notch ligands and receptors regulate V2 interneuron progenitor proliferation and V2a/V2b cell fate determination, 196-206, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.