- Title
-
p35 promotes the differentiation of amacrine cell subtype in the zebrafish retina under the regulation of egr1
- Authors
- Zhang, L., Bonilla, S., Zhang, Y., and Leung, Y.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
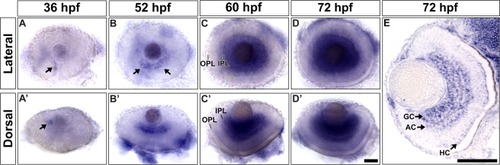
The expression dynamics of p35 during zebrafish retinogenesis. A time-series whole-mount in situ hybridization was performed to detect the expression pattern of p35 in WT retina. The resulting eyes were dissected and imaged from the lateral and dorsal views. The signal of p35 was first detected in an anterior-ventral patch of the retina at around 36 hpf (A, A′; arrow). Then, it spread towards the dorsal side of the GCL and was mainly detected in this region at 52 hpf (B, B′; arrows). By 60 hpf, p35′s staining was detected in the GCL and AC region (C, C′). Faint staining in the apical INL began to appear at this stage, and became more conspicuous at 72 hpf (D, D′). This signal originated from HCs, as revealed by cryosectioning of the embryos at the same stage (E). In addition, the staining in the GCL and AC region became stronger than the earlier stages. GC, ganglion cells; AC, amacrine cells; HC, horizontal cells; IPL, inner plexiform layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer. For A–D, anterior is to the left and dorsal is up; for A′–D′, anterior is to the left and lateral is up; for E, lateral is to the left and dorsal is up. Scale bars = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
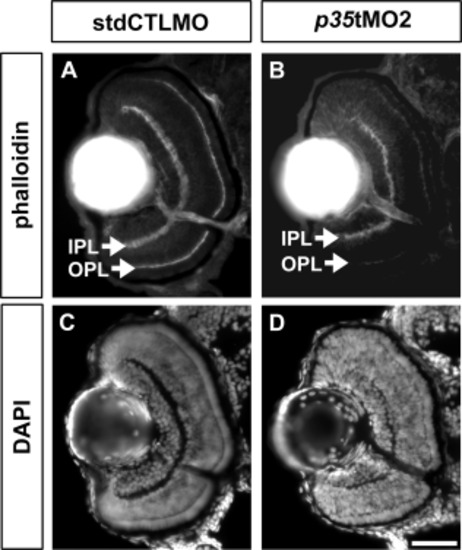
Retinal differentiation was affected by p35 knockdown at 72 hpf. The retinal histology of the p35 morphants (p35 tMO2) and controls (stdCTLMO) was analyzed at 72 hpf. At this stage, the phalloidin staining highlighted IPL and OPL with a sharp and distinct boundary in the controls (A), while these plexiform layers were thinner and irregular in the p35 morphants (B). A similar observation of the plexiform layer formation was also revealed by the DAPI nuclei staining on the same sections (C, D). IPL: inner plexiform layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer. Scale bar = 50 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
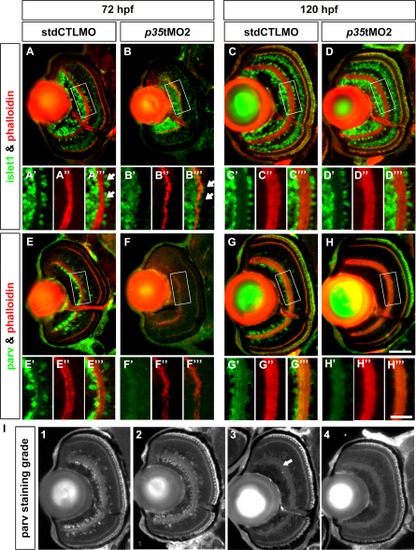
p35 knockdown compromised the differentiation of Parv+ but not Islet1+ ACs. Immunohistochemical analysis of ACs in the controls (stdCTLMO) and p35 morphants (p35tMO2) was performed with anti-Islet1 (Islet1; A–D) and anti-Parvalbumin (Parv; E–H) for cholinergic and a subset of GABAergic ACs, respectively, at 72 and 120 hpf. These markers are shown in green, while the plexiform layers are highlighted by phalloidin in red. A magnified view of the white box is shown at the bottom of each whole retinal section. For Islet1+ ACs, they were not aligned regularly on the boundary of the apical IPL at 72 hpf (A′′′, B′′′; white arrows). In addition, their numbers were also reduced. By 120 hpf, these differentiation problems were largely resolved and the two conditions became comparable (C-C′′′ and D-D′′′), indicating that the effect was caused by a developmental delay. Interestingly, Parv+ ACs were almost absent in the p35-morphant retinas compared with the controls at 72 hpf (E-E′′′ and F-F′′′) and was still substantially reduced at 120 hpf (G-G′′′ and H′-H′′′). The differentiation defects of these ACs likely contributed to the thinning of the IPL at 72 hpf. In addition, the reduction of Parv signal at 120 hpf was quantified as described in the Experimental Procedures section and Table 1. I: An example of the four different staining grades. The white arrow in grade 3 indicates a small region with positive Parv projections detected in the IPL. For A–H: The cryosection of a whole retina is shown at the top and a magnified view of the white box in the central retina is shown at the bottom. For the whole retinal images, lateral is to the left and dorsal is up. Scale bars for the whole retinal section and magnified view were 50 and 25 μm, respectively. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
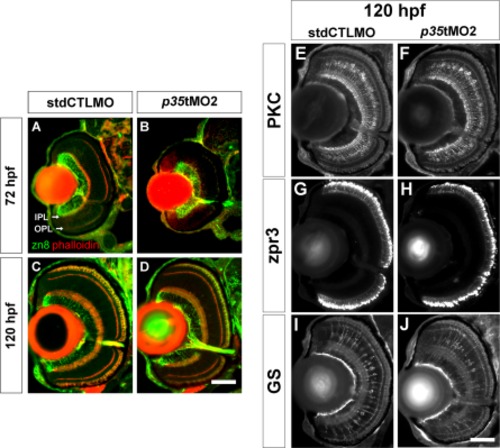
The differentiation of GCs, BCs, rods, and MCs appeared normal in the p35-morphant retinas. A–D: Immunohistochemical analysis of GCs in the controls (stdCTLMO) and p35 morphants (p35tMO2) was performed with anti-zn8 (zn8) at 72 and 120 hpf. The zn8 signal is shown in green, while the plexiform layers are highlighted by phalloidin in red. At 72 hpf, the number of GCs, as counted by the DAPI nuclei with positive zn8, was not different between the control and p35-morphant retinas (A, B). This result suggests that the formation of GCs was not affected by p35 knockdown. Even though the dendritic projections of GC appeared compromised in the p35-morphant retinas at this stage, the overall zn8 staining pattern between the control and p35-morphant retinas was comparable at 120 hpf (C, D). These observations suggest that the GC differentiation was normal by this stage. E–J: Immunohistochemical analysis of BCs, rods, and MCs in the controls and p35 morphants was performed with anti-PKC βI (PKC), anti-zpr3 (zpr3), anti-GS (GS) at 72 hpf (data not shown) and 120 hpf. The p35 knockdown substantially reduced the staining signal of these markers in the p35-morphant retinas compared with the controls at 72 hpf. However, the staining became very comparable between the two conditions at 120 hpf. In these images, lateral is to left and dorsal is up. IPL: inner plexiform layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer. Scale bars = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
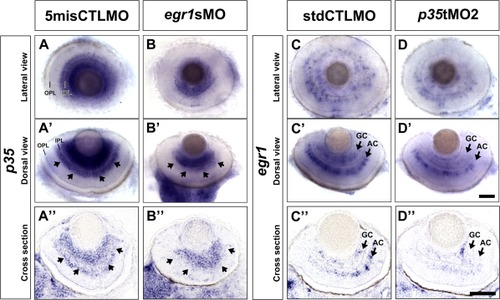
p35 expression in the AC region of the Egr1-morphant retinas was severely reduced, while egr1 expression in the p35-morphant retinas was modestly attenuated. A,B: Whole-mount in situ hybridization of p35 was performed with the control- (5misCTLMO) and Egr1-morphant (egr1sMO) embryos at 72 hpf. The p35 signal was generally reduced in the Egr1-morphant retinas (B, B′) compared with the controls (A, A′), and it was significantly reduced in the AC region (arrows in A′, B′). The latter was particularly obvious on the sectioned retinas (A′′, B′′). C,D: Whole-mount in situ hybridization of egr1 was performed with the control- (stdCTLMO) and p35-morphant (p35 tMO2) embryos. In the controls, egr1 was strongly expressed in the GCL and AC region at 72 hpf (C-C′′; arrows), while in the p35 morphants, egr1 signal was reduced in the GCL and AC region (D-D′′; arrows). Nonetheless, the overall signal reduction in the AC region in the whole-mount retinas was relatively less drastic than that in the GCL (C′, D′). For the lateral view of the dissected eyes in A-D, anterior is to the left and dorsal is up; for the dorsal view in A′-D′, anterior is to the left and lateral is up; while for the cross-section in A′′- D′′, dorsal is to the left and lateral is up. GC, ganglion cell; AC, amacrine cell; IPL, inner plexiform layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer. Scale bars = 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|