- Title
-
Subtractive phage display technology identifies zebrafish marcksb that is required for gastrulation
- Authors
- Wang, Y.W., Wei, C.Y., Dai, H.P., Zhu, Z.Y., and Sun, Y.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene
|
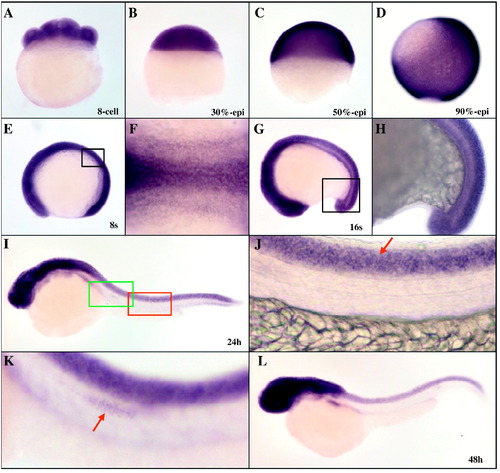
Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of zebrafish marcksb during early development. A: 8-cell stage; B: 30%-epiboly stage; C: 50% epiboly stage; D: 90% epiboly stage; E and F: 8 somites stage; G and H: 16 somites stage; I-K: 24 hpf; L: 48 hpf. J: partial enlargement of panel I, arrow indicates the spinal cord; K: partial enlargement of panel I, arrow indicates the lateral line progenitor neurons. Embryos in A -D were lateral view with dorsal to the right, embryos in E, G-L were lateral view with dorsal to the top, and embryo in F was dorsal view with anterior to the left. |
|
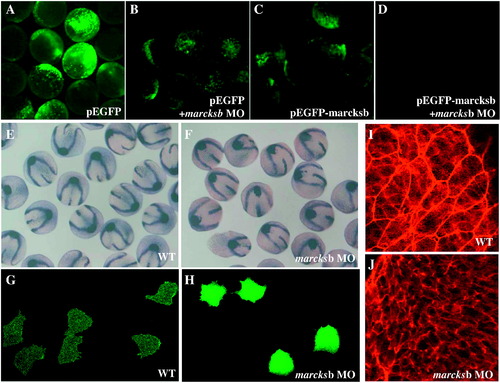
Zebrafish marcksb is required for gastrulation movements through regulation of cell membrane protrusion and F-actin alignment. A: pEGFP injected embryos; B: pEGFP and marcksb MO co-injected embryos; C: pEGFP-marcksb injected embryos; D: pEGFP-marcksb and marcksb MO co-injected embryos; E: ntl, dlx3 and hgg1 labeled wildtype embryos; F: ntl, dlx3 and hgg1 labeled marcksb MO injected embryos; G: visualization of membrane protrusion in wildtype embryos; H: visualization of membrane protrusion in marcksb MO injected embryos; I: visualization of F-actin alignment in wildtype embryos; J: visualization of F-actin alignment in marcksb MO injected embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Gene, 521(1), Wang, Y.W., Wei, C.Y., Dai, H.P., Zhu, Z.Y., and Sun, Y.H., Subtractive phage display technology identifies zebrafish marcksb that is required for gastrulation, 69-77, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene