- Title
-
Two dynamin-2 genes are required for normal zebrafish development
- Authors
- Gibbs, E.M., Davidson, A.E., Trickey-Glassman, A., Backus, C., Hong, Y., Sakowski, S.A., Dowling, J.J., and Feldman, E.L.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
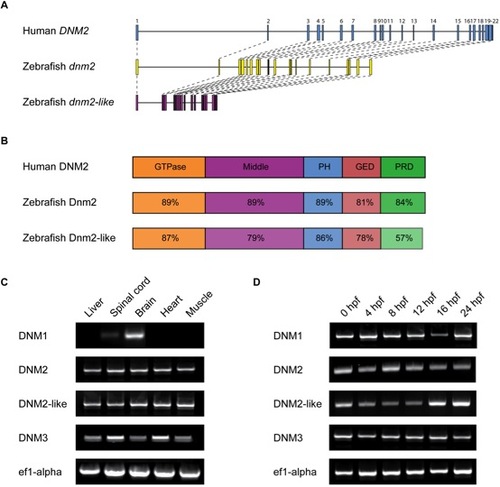
Structure and expression of dnm2 and dnm2-like.(A) Molecular intron-exon organization of human DNM2, zebrafish dnm2 and zebrafish dnm2-like. (B) Protein structure of zebrafish Dnm2 and Dnm2-like compared to human DNM2. Percent identity between zebrafish and human protein domains was calculated using BLASTP. PH, pleckstrin homology domain; GED, GTPase effector domain; PRD, proline-rich domain. (C) RT-PCR was used to assay spatial expression levels of dnm2 and dnm2-like in tissues isolated from adult zebrafish. Primers for ef1α were used as an internal control. (D) RT-PCR was used to assay temporal expression levels of dnm2 and dnm2-like between 0 hpf and 24 hpf. All classical dynamins appear to be deposited as maternal mRNAs and expressed throughout early development. |
|
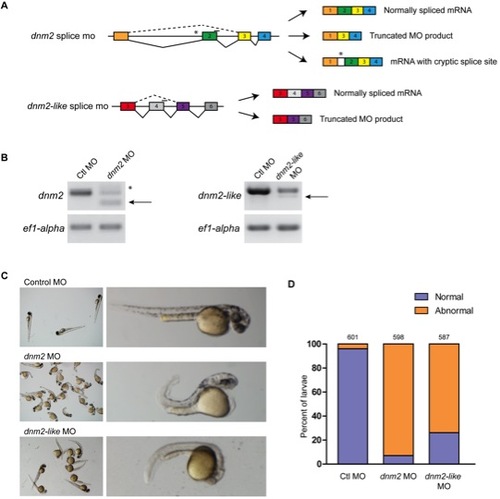
Morpholino-mediated knockdown of dnm2 and dnm2-like expression results in morphological changes.(A) Splice targeting morpholinos were designed against intron-exon boundaries within the dnm2 and dnm2-like genes. (B) Knockdown in morpholino injected embryos was verified using RT-PCR. Embryos were injected with a scrambled control morpholino (Ctl MO; 0.3 mM), dnm2 MO (0.3 mM), or dnm2-like MO (0.1 mM). Arrows indicate the alternative splice product induced by dnm2 MO and dnm2-like MO injection. dnm2 MO injection also resulted in an additional higher weight band due to activation of a cryptic splice site (*). (C) At 2 dpf, dnm2 MO-injected embryos exhibit shortened body length, upward curled tails, pericardial and yolk edema, and reduced head size when compared to control morpholino injected embryos. By contrast, embryos injected with dnm2-like MO have small muscle compartments, pigmentation defects, and mild tail curvature. (D) Percent of affected embryos at 2 dpf (ctl MO vs. dnm2 MO p<0.0001, ctl MO vs. dnm2-like MO p<0.0001; Fisher?s exact test). The total number of embryos is noted above each bar. |
|
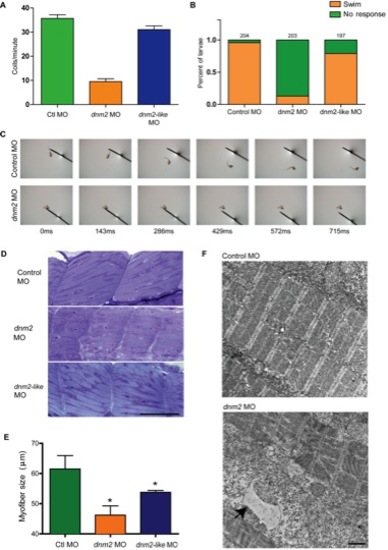
Knockdown of dnm2 results in motor deficits and abnormal muscle histology.(A) Quantitation of spontaneous embryo coiling at 1 dpf. On average, control morphants coiled 35.7 times in 60 seconds, while dnm2 morphants coiled only 9.5 times. (B-C) Touch-evoked swimming was measured in 3 dpf morphants. Most control and dnm2-like morphants responded to tail taps with a rapid escape response, while dnm2 morphants exhibited impaired escape responses. (D) Toluidine blue stained semi-thin sections from 3 dpf morphants. Somites from dnm2 morphants are small with highly disorganized myofibers. Scale bar is equal to 50 μm. (E) Quantification of myofiber length in 3 dpf embryos. Average myofiber size in control embryos equaled 87.8 μm, while dnm2-like morphants equaled 76.8 Ám and dnm2 morphants equaled 66.0 μm (*p<0.05 ctl to dnm2-like, *p<0.01 ctl to dnm2, p = 0.056 dnm2 to dnm2-like morphants; ANOVA ). (F) Representative electron micrographs from larval dnm2 morphant muscle. Irregular membrane structures were found throughout the muscle (black arrow). Scale bar is equal to 1 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
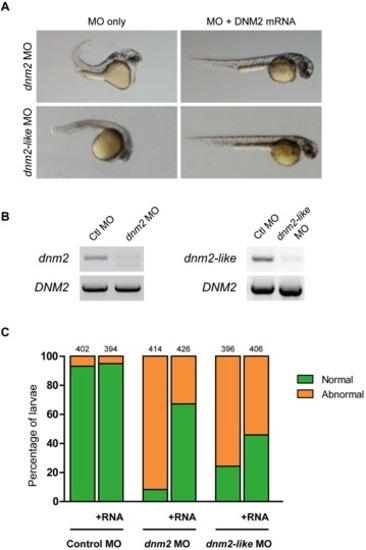
Human DNM2 RNA rescues dnm2 and dnm2-like morphant phenotypes.Rescue of dnm2 and dnm2-like morphants at 2 dpf. (A) Co-injection of human DNM2 RNA can rescue morphological abnormalities in both morphants. (B) RT-PCR of human DNM2 expression in dnm2 or dnm2-like morphants at 3 dpf. (C) The percentage of normal appearing larvae is significantly increased in both dnm2 and dnm2-like rescue conditions, but not in control larvae (dnm2 p<0.0001, dnm2-like p<0.0001, ctl p = 0.30; Fisher?s exact test). The total number of embryos is noted above each bar. |
|
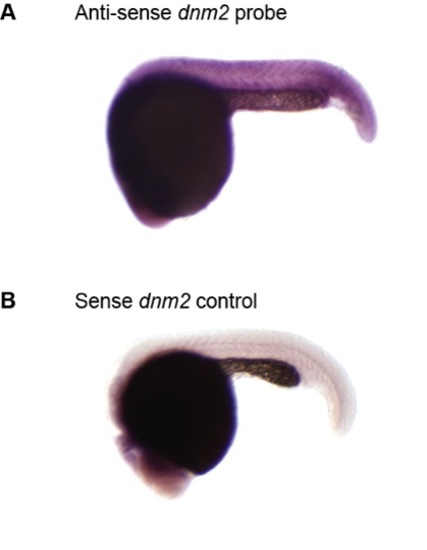
Zebrafish dnm2 whole mount in situ hybridization. (A) Whole mount in situ of 1 dpf embryos reveals ubiquitous expression of dnm2. (B) Sense probe to dnm2 was used as a background control. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|