- Title
-
The Cell Neural Adhesion Molecule Contactin-2 (TAG-1) Is Beneficial for Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury in Adult Zebrafish
- Authors
- Lin, J.F., Pan, H.C., Ma, L.P., Shen, Y.Q., and Schachner, M.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
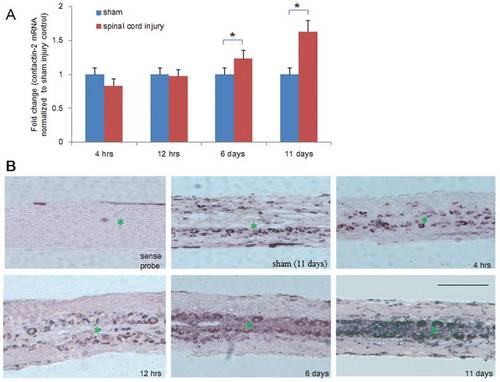
Time course of contactin-2 mRNA expression after spinal cord injury. (A) Quantitative PCR (qPCR) shows expression of contactin-2 mRNA in the spinal cord caudal to the lesion site at four time points after SCI. Significant upregulation was observed at 6 and 11 days after SCI compared to the sham injury group (*p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey?s post-hoc test; n = 8 fish/group). Values represent means+SEM. (B) In situ hybridization detection of contactin-2 mRNA in longitudinal sections of the spinal cord 3 mm caudal to the lesion site at 4 and 12 hrs, and at 6 and 11 days after SCI (n = 3 fish/group). Numbers of positive cells were increased along the central canal at 6 and 11 days after SCI compared to the sham injury group at 11 days. No signal was detected in sections incubated with a sense probe. * indicates the central canal. Scale bar, 400 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
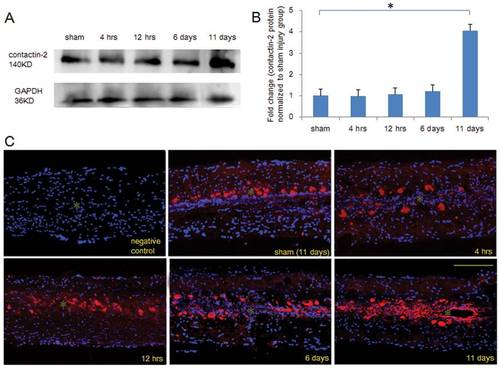
Time course of contactin-2 protein expression after spinal cord injury. (A) Western blot analysis shows contactin-2 protein expression in the spinal cord caudal to the lesion site at four time points after SCI. Significant upregulation was detected at 11 days after SCI compared to the sham injury group at 11 days. (B) The intensity of bands as quantified by ImageJ software and fold change compared with the sham injury group shows an increase in contactin-2 protein level that achieved significance at 11 days after SCI (*p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey?s post-hoc test; n = 5 fish/group). Values represent means+SEM. (C) Contactin-2 expression in the spinal cord 3 mm caudal to the lesion site was examined by immunofluorescence in longitudinal sections at 4 and 12 hrs, and at 6 and 11 days after SCI. Upregulation of contactin-2 was mainly observed along the central canal at 11 days after SCI. Negative control (without primary antibody), contactin-2 (red), DAPI (blue). * indicates the central canal. Scale bar, 200 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Contactin-2 protein expression is upregulated by motoneurons along the central canal after spinal cord injury. Double immunolabeling of contactin-2 with islet-1 in longitudinal sections (3 mm caudal to the lesion site) shows that in the spinal cord of non-injured zebrafish, contactin-2 is prominently expressed by motoneurons and other cell types. At 11 days after SCI, contactin-2 expression is increased compared to non-injured fish along the central canal. * indicates the central canal. Scale bar, 200 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
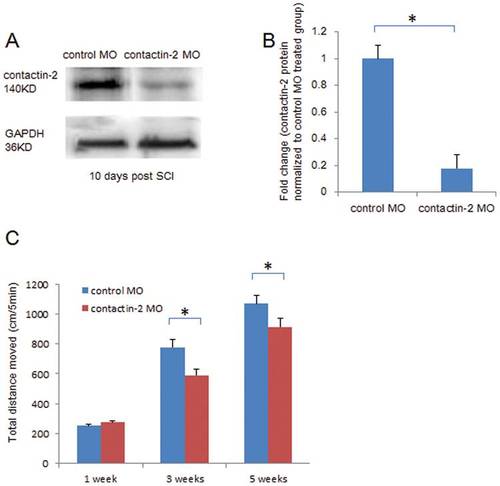
Knock down of contactin-2 expression after spinal cord injury retards locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury. (A) Contactin-2 protein expression is reduced at 10 days after SCI by application of contactin-2 antisense morpholino (MO) as detected by Western blot analysis. (B) Intensity of the bands as quantified by ImageJ software, and fold change compared with control MO treated group shows a decrease in contactin-2 protein level at 10 days after application of contactin-2 MO (*p<0.05, Student?s t-test; n = 5 fish/group). Values represent means+SEM. (C) Total distance moved in 5 min of undisturbed zebrafish treated with contactin-2 MO or control MO (n = 8 fish/group) after SCI. At 3 and 5 weeks after SCI, the total distance moved was reduced by treatment with contactin-2 MO when compared to fish treated with control MO (*p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Student-Newman-Keuls test; n = 8 fish/group). Values represent means+SEM. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
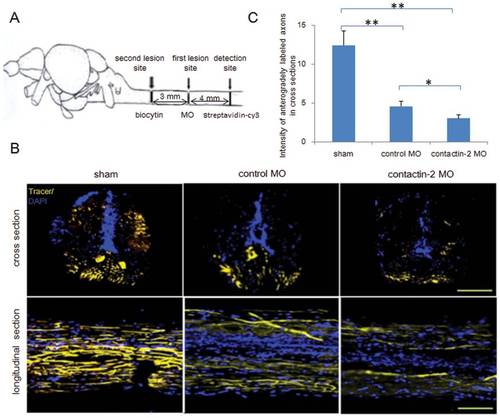
Reduction of contactin-2 protein expression after spinal cord injury impairs regrowth of axons. (A) Schematic illustration for anterograde tracing. Biocytin was applied at the site symbolized by the second lesion site at 6 weeks after the first lesion. After 24 hrs, biocytin was detected at the site 4 mm distal to the first lesion site by Streptavidin-Cy3. (B) Cross and longitudinal sections show axons regrown beyond the first lesion site. (C) Relative fluorescence intensity for cross sections was quantified by ImageJ software. A 34% decrease in intensity was observed in the contactin-2 anti-sense MO treated group compared to the control MO treated group (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, t-test; n = 3 fish/group). The sham injury group shows similar intensities as the non-injury group. Scale bars, 200 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
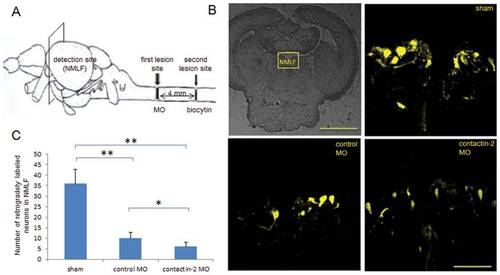
Reduction of contactin-2 protein expression after spinal cord injury impairs axon regrowth of NMLF neurons. (A) Schematic illustration for retrograde tracing. Biocytin was applied at the site symbolized by the second lesion site at 6 weeks after the first lesion, and was detected in the NMLF after 24 hrs using Streptavidin-Cy3. (B) Retrogradely labeled neurons in the NMLF. (C) Numbers of retrogradely labeled neurons in the NMLF. Reduction of contactin-2 protein expression by application of contactin-2 anti-sense MO reduces the numbers of NMLF neurons with axons regrown beyond the first lesion site when compared to the control MO treated group (*p<0.05, t-test; n = 3 fish/group). The sham injury group shows similar numbers of retrogradely labeled neurons as the non-injury group. Scale bars, 200 μm and 50 μm. |