- Title
-
Midkine-A functions upstream of Id2a to regulate cell cycle kinetics in the developing vertebrate retina
- Authors
- Luo, J., Uribe, R.A., Hayton, S., Calinescu, A.A., Gross, J.M., and Hitchcock, P.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Neural Dev.
|
Mdka -targeted morpholinos inhibit Mdka synthesis and delay neuronal differentiation. (A) Sequences of the two morpholino oligos (MO1, MO2) and the respective mismatch (MM) controls used in this study. (B) Representative embryos from the control and experimental groups at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf). (C) Western blot prepared from 48 hpf embryos. MM, embryos injected with 5-nucleotide mismatch control morpholinos; MO, embryos injected with MO1 Mdka- targeted morpholinos; UI, uninjected control. Note the absence of protein in embryos injected with the mdka-targeted morpholinos (similar results were observed using MO2.) The upper bands are stained with antibodies against actin and serve as loading controls. (D) (a, d, g) Sections taken through the retinas of uninjected embryos (UI) at 48 hpf and stained with antibody markers for ganglion cells (zn12; zn5) and amacrine cells (HPC-1), respectively. (b, e, h) Sections of retinas of embryos injected with 5-nucleotide mismatch morpholinos (MM1) and immunostained as above. (c, f, i) Retinas of embryos injected with Mdka translation-blocking morpholinos (MO1) and immunostained as above. Note the absence of differentiation markers that label inner retinal neurons. (E) Representative sections from uninjected (a), control (b), and loss-of-function embryos (c) allowed to survive to 72 hpf. The absence of neuronal differentiation at 48 hpf is recovered by 72 hpf. gcl, ganglion cell layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; L, lens; ON, optic nerve; onl, outer nuclear layer; . Scale bar equals 50μm. MIP 3D; Maximum intensity projection, three dimensional. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Loss of Mdka function does not affect neurogenic competence or increase cell death. (A) In situ hybridizations showing atoh7 expression in the retinas of uninjected (a-c), control (d-f) and Mdka loss-of-function embryos (g-i). Arrows in panels a, d and g identify the initial cluster of atoh7-expressing cells in ventral retina. MM, embryos injected with 5-nucleotide mismatch morpholinos; MO, embryos injected with mdka-targeted morpholinos; UI, uninjected. Scale bar equals 50μm. (B) Average number of acridine orange-stained cells in the retinas of control and experimental embryos showing that loss of Mdka does not increase cell death. P >0.05 for all pairwise comparisons. n=5 to 7 embryos/time point. Scale bar equals 50 μm. |
|
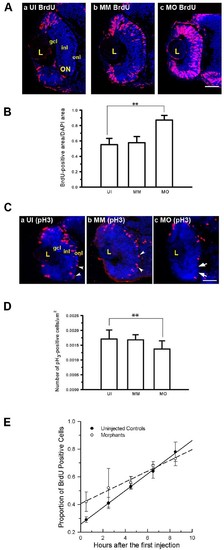
Mdka loss-of-function alters cell cycle kinetics. (A) BrdU labeled progenitors in uninjected (a) control (b) and Mdka loss-of-function embryos (c). (B) Histograms showing the average proportion of the retinal section occupied by BrdU-labeled cells. *P <0.001. n = 9 retinas/group. Scale bar equals 50μm.(C) Retinas of embryos at 48 hpf stained with antibodies against phosphohistone H3 (pH3) in uninjected (a), control (b), and Mdka loss-of-function embryos (c). (D) The number of pH3-stained cells/unit area. **P <0.01. n=12 embryos/group. MM, embryos injected with 5-pair mismatch control morpholinos; MO, embryos injected with mdka-targeted morpholinos (MO); UI, uninjected embryos. gcl, ganglion cell layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; L, lens; ON, optic nerve; onl, outer nuclear layer. Scale bar equals 50 μm. (E) Graph of the least-squares regression lines through data showing the proportion of BrdU-labeled progenitors as a function of time. An F-test was used to compare the control and experimental data. **P <0.05. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
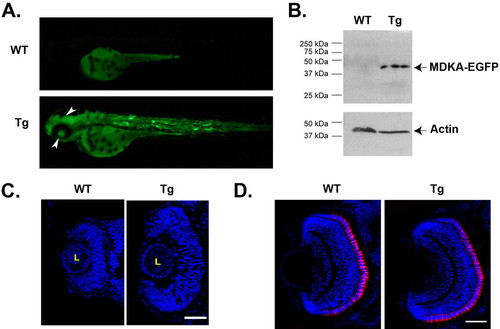
Conditional over-expression of Mdka. (A) Induced fluorescence in a Tg(pHSP70/4:mdka:egfp) larva at 72 hpf after heat shock treatment at 24 hpf. (B) Western blot stained with antibodies against EGFP showing induction of the fusion protein at 72 hpf after heat shock at 24 hpf. Tg, heat shock-treated, transgenic siblings; WT, heat shock-treated, wild-type embryos. (C) Mdka gain of function results in marked retinal overgrowth at 30 hpf, which is largely resolved by 72 hpf (D). Tg, heat shock-treated embryos from the Tg(pHSP70/4:mdka:egfp) line; WT, heat shock-treated wild-type siblings. Scale bar equals 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
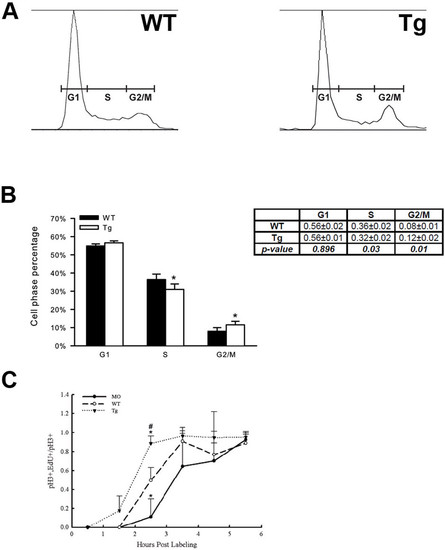
Mdka gain-of-function accelerates the cell cycle. (A) Representative raw data from FACS sorting of neural progenitors at 30 hpf. (B) Histograms showing the average percentage of cells in the G1-, S-, and G2-/M- phases of the cell cycle. *P <0.01. n=4 independent assays from a minimum of 5,000 cells/assay. (C) Graph showing the percent labeled mitoses for embryos between 28 hpf and 34 hpf. #*P <0.01. n=4 embryos/condition/time point. MO, embryos injected with mdka-targeted morpholinos; Tg, homozygous transgenic siblings treated with heat shock at 24 hpf; WT, untreated wild-type embryos. |
|
Mdka functions upstream of Id2a. (A) Wholemount in situ hybridizations showing id2a expression at 28 hpf. Embryos were uninjected (Uninjected), injected with mismatch Mdka morpholinos (Control MO), Mdka translation-blocking morpholinos (Mdka l-o-f), or transgenic embryos treated with heat shock at 24 hpf (Mdka g-o-f). The letter ?e? identifies the eye. Note that id2a expression is modulated by Mdka levels. (B) Representative control and experimental embryos at 48 hpf. Embryos were uninjected (Control), injected with id2a mRNA (id2a), Mdka translation-blocking morpholinos (MdkaMO), or co-injected with Mdka translation-blocking morpholinos and id2a mRNA. (C) Representative retinal sections from embryos at 48 hpf. The conventions are as above. Sections are stained with DAPI to label nuclei and antibodies against phosphohistone H3. (D) Graph showing the number of retinal cells in each group. (E) Graph showing the number of phosphohistone H3-positive cells in each group. Note that the number of DAPI and phosphohistone H3-positive cells are reduced following Mdka l-o-f and cell numbers are restored following co-injections of Mdka translation-blocking morpholinos and id2a mRNA. **P <0.05. Scale bars in panel B and C are 200 μm and 50 μm, respectively. |
|
Expression of id2a at 28hpf.In situ hybridization of wholemount embryos at 28 hpf recapitulates the tissue-specific pattern of id2a expression (cf. Figure 3, Thisse et al., 2004). Scale bar equals 100 μm L, lens. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
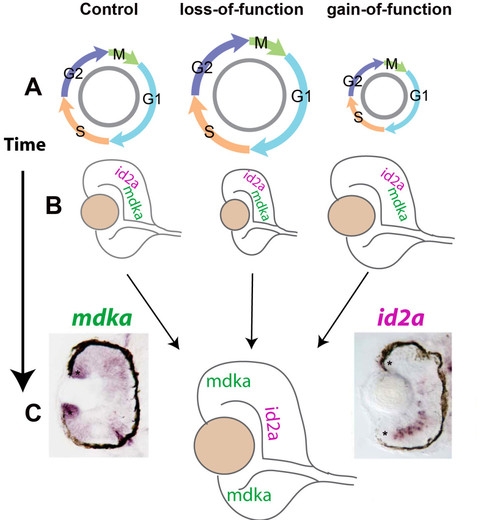
Summary diagram. The level of Mdka synthesis systematically alters the length of the cell cycle, as indicated by the diameter of the cell cycle cartoons (A), and the size of the eye (B). This corresponds also to the early expression of both mdka and id2a in retinal progenitors (B). By 48 hpf, mdka and id2a are differentially expressed in retinal progenitors and INL neurons, respectively, which is most evident for cells at the retinal margin (asterisks, C). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|