- Title
-
Olig2-expressing hindbrain cells are required for migrating facial motor neurons
- Authors
- Zannino, D.A., Sagerström, C.C., and Appel, B.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
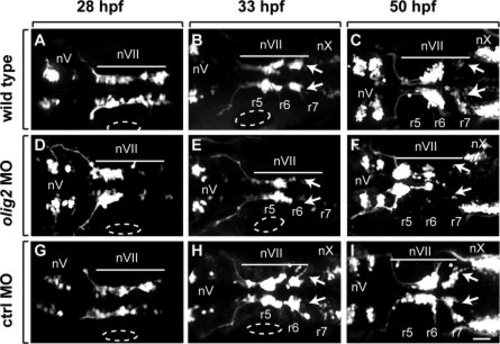
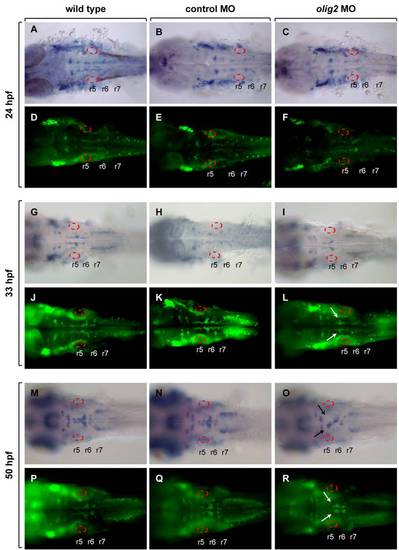
Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 reporter expression reveals a facial motor neuron migration defect in olig2 MO-injected embryos as compared to wild-type and control MO-injected embryos. Panels are z-stack images showing dorsal views of whole embryos with anterior to the left. A?C: Wild-type embryos. D?F:olig2 MO-injected embryos. G?I: Control MO-injected embryos. Arrows indicate posteriorly migrated facial motor neurons. Bar indicates facial motor neurons along their caudal migration. Cranial motor neurons are labeled ?n.? Otic vesicles are outlined. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
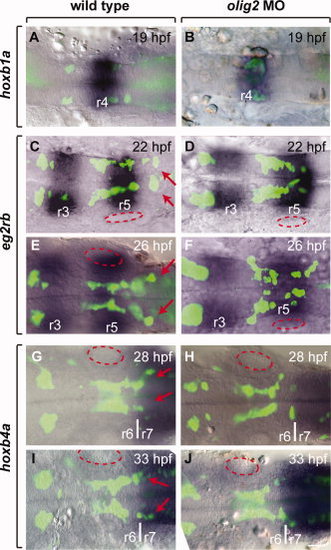
Facial motor neurons fail to completely exit r4 and r5 to form clusters in r6 and r7. Panels show a single z-plane image of dorsally mounted whole embryos with anterior to the left. Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 reporter expression, amplified using an anti-GFP antibody and an Alexa 488 secondary antibody, is revealed as green and RNA expression patterns are blue. A,B:hoxb1a expression marks r4. C?F:egr2b expression labels r3 and r5. G?L:hoxb4a expression begins at the r6/r7 boundary and extends posteriorly. Arrows indicate region where facial motor neurons normally migrate. Approximate location of the otic vesicles is outlined with red ovals. Scale bar = 32 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
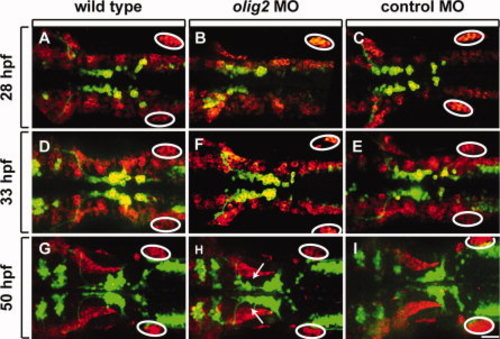
olig2 MO does not disrupt lateral line migration. All panels show dorsal views of whole embryos, anterior to the left. Elavl labeling is shown in red and Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 reporter expression is green. A?C: 28-hpf embryos. D?F: 33-hpf embryos. G?I: 50-hpf embryos. A?F show projections of z-stack images in both red and green channels. The red channel in G?I is a single z-plane, focused on the lateral line, whereas the green channel is a z-stack image projection of the green channel. Circles mark the posterior lateral line primordia. Arrows indicate lagging facial motor neurons in olig2 MO-injected embryos. Scale bar = 30 μm. |
|
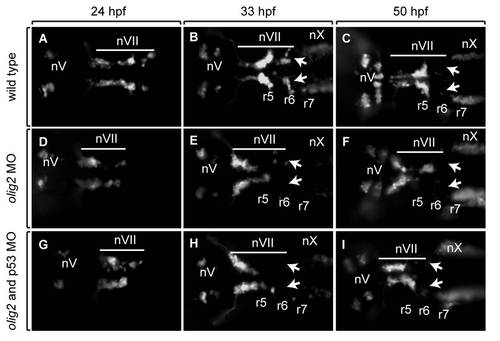
Normal facial motor neuron migration revealed by time-lapse imaging. Panels show frames captured from a time-lapse imaging sequence obtained from a control Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 embryo. Z-stack projection images are shown from dorsal orientation with anterior to the left. Developmental time is indicated in the upper right-hand corner of each panel. Cranial motor neurons are labeled ?n.? Arrows indicate axons of facial motor neurons (nVII). Arrowheads indicate cluster of nVII neurons in r7. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Facial motor neuron migration revealed by time-lapse imaging. Panels show frames captured from a time-lapse imaging sequence obtained from an olig2 MO-injected Tg(isl1:GFP)rw0 embryo. Z-stack projection images are shown from dorsal orientation with anterior to the left. Developmental time is indicated in the upper right-hand corner of each panel. Cranial motor neurons are labeled ?n.? Arrows indicate axons of facial motor neurons (nVII). Asterisks indicate a small number of cells migrating caudally. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
olig2 and sdf1a expression in wild-type, mafba-/- and olig2 MO-injected embryos. All images show dorsal views with anterior to the left. A,B:olig2 expression in wild-type (A) and mafba-/- (B) embryos at 24 hpf. Arrow in B indicates loss of r5/r6 olig2 expression in mafba-/- in mutant embryos. Otic vesicles are outlined in red. C,D:sdf1a (blue) and egr2b (red) expression in wild-type (C) and mafba-/- (D) embryos at 18 hpf. Absence of r5 egr2b expression identifies mafba mutants. E,F:sdf1a expression in wild-type (E) and mafba-/- (F) embryos at 24 hpf. Mutant embryos lack r6 expression (arrow). G?J:sdf1a expression in control (G,I) and olig2 (H,J) MO-injected embryos (H, J). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
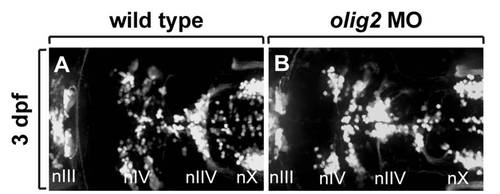
Distribution of branchiomotor neurons marked by Tg(isl1:gfp)rw0 reporter expression at 3 dpf. Dorsa| whole mount with anterior to the left. A: Wild-type embryo. B: olig2 MO-injected embryo. Cranial motor neurons labeled ?n.? |
|
Expression of isl RNA and protein in wild-type, control MO-injected, and olig2 MO-injected embryos. Dorsal whole mount with anterior to the left. A?C: isl1 RNA expression in 24-hpf embryos. D?F: Isl protein expression detected by immunocytochemistry in 24-hpf embryos. G?I: isl1 RNA expression in 33-hpf embryos. J?L: Isl protein expression detected by immunocytochemistry in 33-hpf embryos. M?O: isl1 RNA expression in 50-hpf embryos. P?R: Isl protein expression detected by immunocytochemistry in 50-hpf embryos. Otic vesicles are outlined. |
|
Tg(isl1:gfp)rw0 reporter expression reveals that the facial motor neuron migration defect in olig2 MO-injected embryos is not affected by co-injection of p53 MO. Panels are images showing dorsal views of whole embryos with anterior to the left. A?C: Wild-type embryos. D?F: olig2 MO-injected embryos. G?I: olig2 MO-injected embryos co-injected with p53 MO. Arrows indicate posteriorly migrated facial motor neurons. Bar indicates facial motor neurons along their caudal migration. Cranial motor neurons are labeled ?n.? |
|
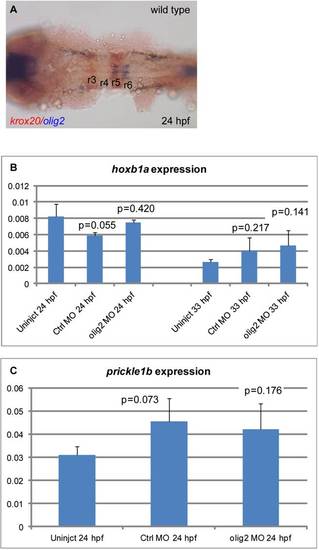
olig2 is not expressed in r4 and olig2 loss of function has no effect on hoxb1a or prickle1b expression. A: Wild-type expression at 22 hpf of olig2 in r5 and r6 in blue and egr2b in r3 and r5 in red. B: qPCR of hoxb1a expression in wild-type, control MO-injected, and olig2 MO-injected embryos at 24 and 33 hpf. C: qPCR of prickel1b expression in wild type, control MO-injected, and olig2 MO-injected embryos at 24 hpf. Error bars represent standard deviation. P value calculated by Student′s t-test is listed above each bar and compared to wild-type embryos. |
|
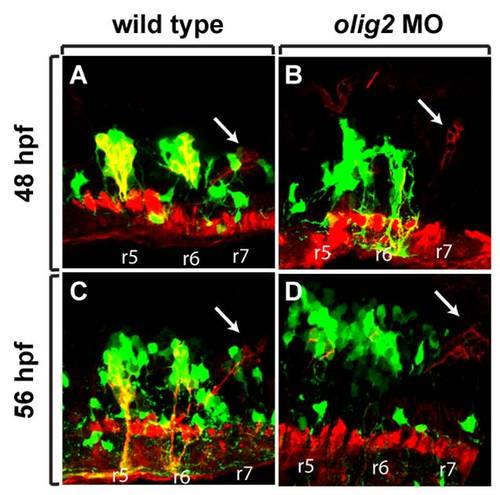
Glossopharyngeal motor neuron formation does not require olig2 function. Tg(olig2:EGFP) embryos labeled with anti-Alcama antibody (red) in wild-type and olig2 MO-injected embryos. Lateral sections, dorsal to the top, anterior to the left. A,B: Wild-type embryos. C,D: olig2 MO-injected embryos. Glossopharyngeal motor neurons indicated by arrows. Rhombomeres labeled ?r.? |