- Title
-
The developing lamprey ear closely resembles the zebrafish otic vesicle: otx1 expression can account for all major patterning differences
- Authors
- Hammond, K.L., and Whitfield, T.T.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
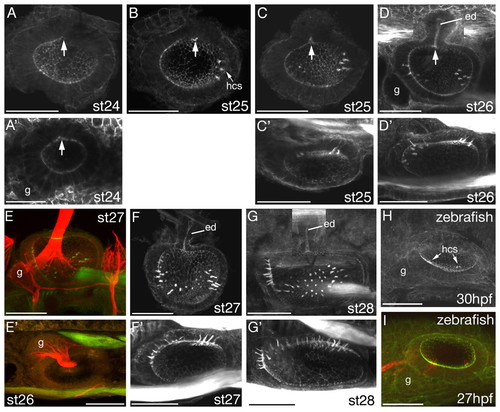
Early development of the lamprey otic vesicle. (A-I) Projections of confocal z-stacks of embryos stained with FITC-phalloidin, revealing the actin-rich stereocilia of the sensory hair bundles and the general morphology of the developing lamprey inner ear. All images are of L. fluviatilis, except for A' (L. planeri) and H,I (zebrafish). (A-I,A') Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal to the top; (C'-G') dorsal views, anterior to the left, medial to the top. (A-C,E,F) Partially dissected specimens; (D,G) composites of two images. Arrows indicate outpocketing of endolymphatic duct. g, statoacoustic (VIIIth) ganglion; ed, endolymphatic duct; hcs, sensory hair cells. (E,E',I) Double stains with FITC-phalloidin (green) and anti-acetylated tubulin (red) to reveal neuronal cell bodies and axonal projections of the statoacoustic ganglion (E,E') and sensory hair cell kinocilia (I). Stages are shown for each panel. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
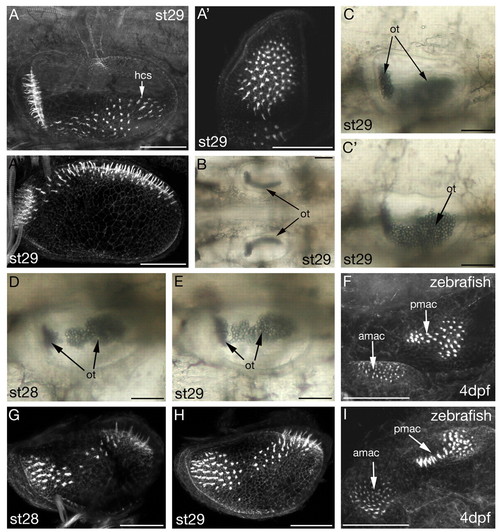
Morphology of stage 28 and 29 L. fluviatilis ears, and comparison with zebrafish. (A-E,G,H) L. fluviatilis; (F,I) zebrafish, focussed medially to reveal maculae. amac, anterior macula; pmac, posterior macula (A-A'',F-I) Projections of confocal z-stacks of FITC-phalloidin-stained ears revealing the actin-rich stereociliary bundles of the sensory hair cells (hcs). (B-E) DIC images of ears in the live lamprey larva. ot, otoconia. (A,C,C',F) Lateral views, anterior to left, dorsal to top; (C,C') different focal planes of the same specimen. (A') Anterior view, dorsal to top, lateral to left. (A'',B) Dorsal views, anterior to left; medial to top in A''; both ears shown in B. (D,E,G-I) Dorsolateral views showing the join region between anterior and posterior areas of the macula; anterior approximately left. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
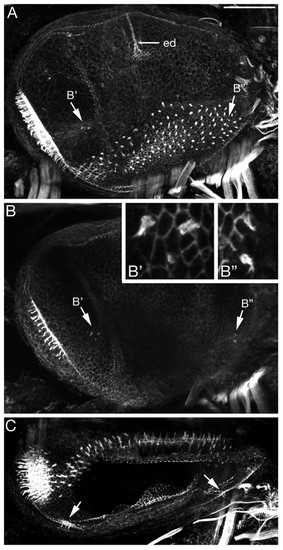
Morphology of the L. fluviatilis otic vesicle at stage 30. (A-C) Projections from confocal z-stacks of a FITC-phalloidin-stained ear showing the actin-rich sensory hair cell stereociliary bundles and general morphology. (A,B) Lateral views, anterior to left, dorsal to top; both are composites of two images. ed, endolymphatic duct. (B) A projection from a lateral subset of the confocal z-stack to show the presumptive cristae clearly, also shown at higher power in insets (B',B''). (C) Dorsal view, anterior to left, medial to top; arrows indicate hair cells in the developing cristae. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
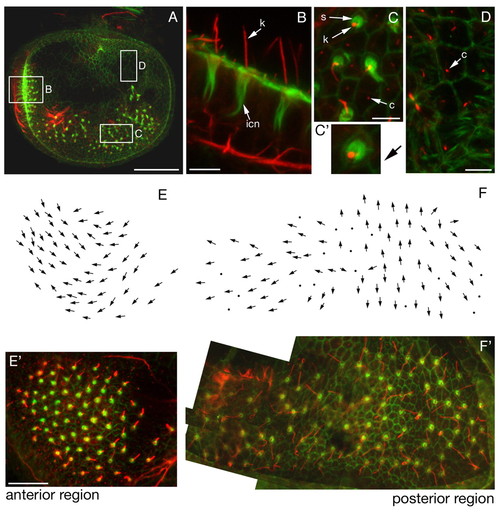
Hair cell polarity in the macula communis of the L. fluviatilis ear at stage 29. (A-D) Projections from confocal z-stacks of FITC-phalloidin (green) and anti-acetylated tubulin (red) double stains revealing the actin-rich stereocilia and the tubulin-rich kinocilia of the sensory hair cells, respectively. (A) Lateral view of whole dissected-out inner ear; regions shown in boxes are the areas shown in detail in B, C and D. (B,C) Lateral (B) and dorsal (C) views of sensory epithelium showing the actin-rich infracuticular network (icn), the short apical horseshoe of stereocilia (s), the long kinocilia (k) and the short cilia (c) on non-sensory cells. (C') Arrow, pointing from the stereociliary bundle towards the kinocilium, shows the polarity of one of the hair cells shown in C. (D) Non-sensory epithelium showing the short cilia (c) present on all non-sensory cells. (E,F) Polarity map of the anterior (E) and posterior (F) regions of the macula communis. (E',F') Stained and dissected specimen used to produce the map shown in E,F. F' is a composite of several images taken in different focal planes. Scale bars: in A, 50 μm; in B-D, 5 μm; in E,F, 25 μm. |
|
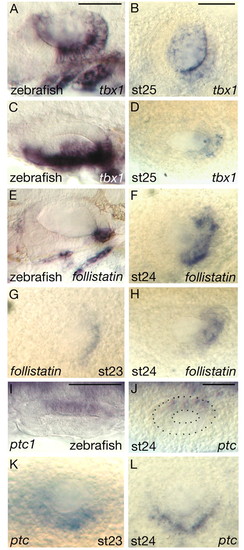
Comparison of mRNA expression patterns. (A-L) Comparison of the mRNA expression patterns of tbx1, follistatin and ptc in zebrafish and lamprey (P. marinus) otic vesicles. (A,C) 28 hpf zebrafish; (E) 30 hpf zebrafish; (I) 20 hpf zebrafish; all others are P. marinus at the stages shown. (C,D,H-J) Dorsal views, anterior to left, medial to top; all others are lateral views, anterior to left, dorsal to top. The otic vesicle is outlined in J for clarity. Scale bars: in A, 50 μm for A,C,E; in B, 50 μm for B,D,F-H,K,L; in I,J, 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
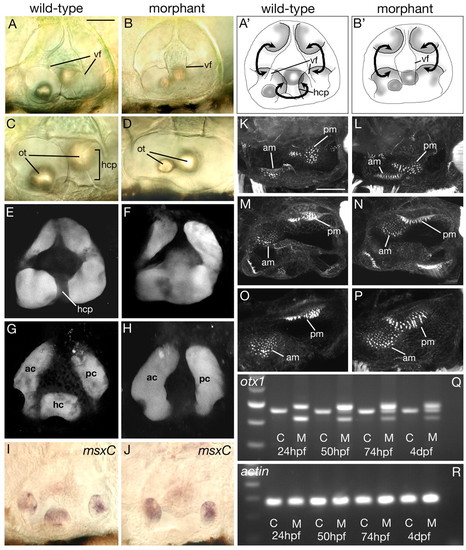
Effects on the developing ear of injection of otx1 morpholino into wild-type zebrafish embryos. (A-D) DIC images of ears of live embryos. (A',B') Schematic representation of ears shown in A,B. Note the lack of the horizontal canal projection (hcp) that delimits the horizontal semicircular canal and the fusion of the two ventral folds (vf) in morphant embryos. The otoliths (ot) of morphants are also closer together than in wild type. Curved black arrows indicate the semicircular canal lumens. (E-H) Confocal sections through ears in which the lumens have been filled with fluorescein-conjugated morpholino. (E,F) Medial sections, in the plane of the semicircular canal projections; (G,H) Lateral sections, in the plane of the lumens of the semicircular canals. ac, anterior canal; pc, posterior canal; hc horizontal canal. (I,J) mRNA expression pattern of msxC marking the cristae. (K-P) Projections of confocal z-stacks of FITC-phalloidin-stained ears revealing the actin-rich stereocilia of the sensory hair bundles. am, anterior macula; pm, posterior macula. (A-L) Lateral views, dorsal to top; (M,N) dorsal views, medial to top; (O,P) junction between anterior and posterior maculae. Anterior is to the left in all panels. All ears are at 96 hpf, except I and J, which are 72 hpf. Scale bars: 50 μm. (Q) RT-PCR across the exon 3/4 boundary. Lane 1, 100 bp ladder; brightest band is 500 bp. (R) RT-PCR using primers to actin. C, control uninjected siblings; M, morpholino-injected embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|