Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240910-56
- Publication
- Burkhalter et al., 2024 - Cilia defects upon loss of WDR4 are linked to proteasomal hyperactivity and ubiquitin shortage
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
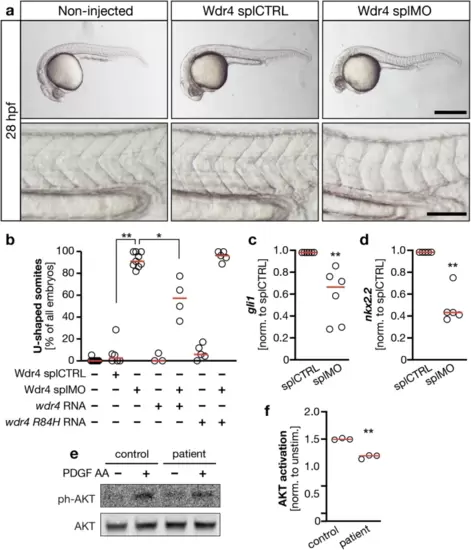
Loss of WDR4 dampens ciliary signaling capacity.a Embryos were left non-injected or were injected with either splCTRL MO or Wdr4 splMO and scored for U-shaped somites at the age of 28 hpf as a read-out for Hedgehog signaling. Only embryos injected with Wdr4 splMO show this defect. Lower panels show same embryos with higher magnification. Scale bars: upper panels 500 Ám, lower panels 100 Ám. b Co-injection of wdr4 RNA partially rescues induction of U-shaped somites upon loss of Wdr4. n = 3?10 experiments with 103?189 embryos. splCTRL vs. splMO **p = 0.0033; splMO vs. splMO + wdr4 RNA *p = 0.015; Kruskal?Wallis test with Dunn?s post-test. c Expression of gli1 in injected zebrafish embryos. Normalized to gapdh and splCTRL. n = 6; **p = 0.0022. Mann?Whitney test. d Expression of nkx2.2 in injected zebrafish embryos. Normalized to gapdh and splCTRL. n = 6; **p = 0.0079. Mann?Whitney test. e WDR4 patient cells show lower capacity for AKT activation upon stimulation with PDGF AA. f Quantification of AKT activation upon stimulation with PDGF AA. Signals were normalized to unphosphorylated AKT and nonstimulated. n = 3; **p = 0.0012. Welch?s t test. Red line: median. |