|
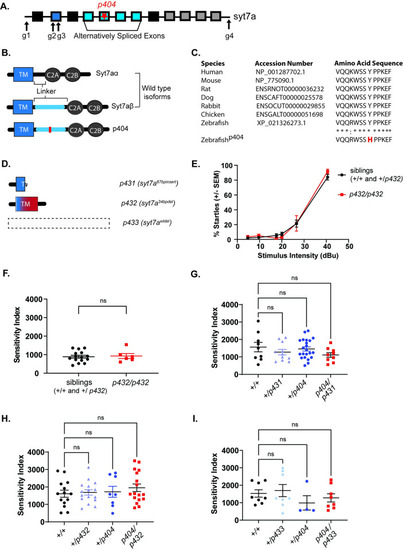
CRISPR-Cas9 generated syt7a mutant alleles complement the escapist p404 mutation. (A) Schematic of syt7a gene. Boxes indicate exons. Exon 2 (dark blue) encodes the transmembrane region of the Syt7a protein. Exons 4–7 are alternatively spliced to produce linker domains of varying lengths. The last four exons encode for the two calcium binding domains, C2A and C2B. Star represents the location of the p404 lesion within the syt7a gene. Arrows indicate regions that were targeted with CRISPR guides for generation of independent mutant alleles. (B) Schematic illustrating the protein structures of two syt7a splicing isoforms: syt7aα and syt7aβ as well as the protein structure resulting from the p404 base pair change within the escapist line. The red line indicates where the missense mutation is located within the syt7aβ isoform. (C) Clustal Omega alignment of the Syt7β protein isoform across different vertebrates. Asterisks (*) represent amino acids that are fully conserved across vertebrates, whereas colons (:) represent amino acids that are similar. Zebrafishp404 results in an amino acid change of a highly conserved Tyrosine (Y) to a Histidine (H) in the syt7aβ isoform. (D) Depiction of predicted protein structures from CRISPR-Cas9-generated syt7a mutant lines. syt7a67bpinsert(p431) and syt7a34bpdel(p432) encode premature stops resulting in a predicted truncated protein of both wildtype isoforms of syt7a. The entire syt7a locus is deleted in syt7awldel(p433), which is predicted to produce no protein in the resulting mutant line. (E) Sensitivity curve for both siblings (n = 15 larvae, black line) and p432 homozygous mutant larvae (n = 6 larvae, red line). X-axis represents the stimulus intensity presented to larvae; Y-axis represents the average percent startles performed by larvae in each group. (F) The area under the curve calculated from the sensitivity curve of both siblings and p432 homozygous mutant individual larvae and plotted as the sensitivity index (AU). Mann-Whitney test was used to compare siblings to p432 mutants (p = 0.9257). (G) Sensitivity Index for complementation testing between escapist line and syt7a67bpinsert(p431) allele. Homozygous WT (+/+, n = 9 larvae), +/p431 (n = 10 larvae), +/p404 (n = 22 larvae), p404 / p431 (n = 9 larvae). Groups were compared by using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. (H) Sensitivity Index for complementation testing between escapist line and syt7a34bpdel(p432) allele. Homozygous WT (+/+, n = 14 larvae), +/p432 (n = 16 larvae), +/p404 (n = 8 larvae), p404 /p432 (n = 17 larvae) Groups were compared by using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. (I) Sensitivity Index for complementation testing between escapist line and syt7awldel(p433) allele. Homozygous WT (+/+, n = 8 larvae), +/p433 (n = 8 larvae), +/ p404 (n = 4 larvae), p404 /p433 (n = 8 larvae). Groups were compared by using a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons.
|