Fig 11
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230406-79
- Publication
- Hong et al., 2023 - Essential role of an ERV-derived Env38 protein in adaptive humoral immunity against an exogenous SVCV infection in a zebrafish model
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
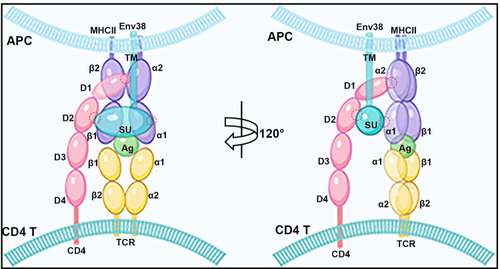
A proposed model of the potential TCR-pMHC-II-CD4-Env38 complex.
The TCR-pMHC-II-CD4-Env38 complex formed in the immune synapse structure between MHC+Env38+ APC and CD4+ T cell during APC-initiated CD4+ T cell activation. Env38 located on the surface of MHCII+ APC in an integral form without undergoing cleavage between the transmembrane subunit (TM) and the surface subunit (SU). Env38 was associated with MHC-II? and CD4 proteins, in which the SU subunit of Env38, the second immunoglobin domain of CD4 (CD4-D2) and the first ?1 domain of MHC-II? chain (MHC-II?1) contribute to the association among Env38, CD4 and MHC-II? proteins. In particular, Env38 specifically binds to CD4-D2 and MHC-II?1 domains without intervention with the CD4-D1 and MHC-II?-?2 as well as CD4-D1 and MHC-II?2 domains, two previously known reciprocal connectors contributing to the formation of the pMHC-TCR-CD4 complex referred as the central supramolecular activating complex (c-SMAC) in the immunological synapse. Hence, Env38 promoted the formation and/or stabilization of pMHC-TCR-CD4 complex via cross-linking MHC-II and CD4 molecules between the MHCII+ APCs and CD4+ T cells. The red circles represented the interaction domains among SU, CD4-D2 and MHC-II?1. |