Figure 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230406-61
- Publication
- Li et al., 2023 - Copper overload impairs hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell proliferation via prompting HSF1/SP1 aggregation and the subsequently downregulating FOXM1-Cytoskeleton axis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
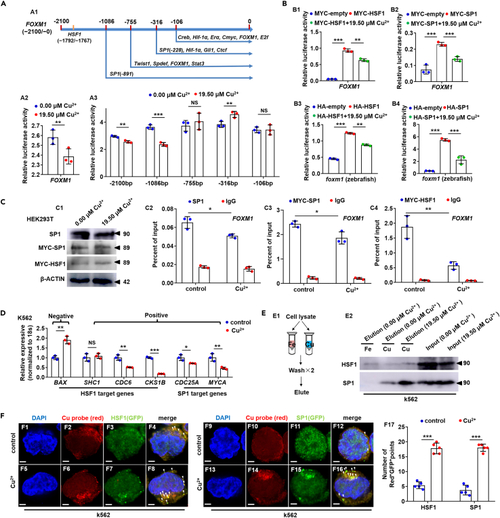
Cu overload impairs HSF1/SP1 transcriptional activities on FOXM1 (A) Schematic diagram of transcription factor targeted domains in FOXM1 promoter (A1), Cu overload significantly suppressed the transcriptional activities of FOXM1 promoters (A2) and transcriptional activities of the 5′ truncated promoters of gene FOXM1 (−2100/+28, −1086/+28, −755/+28, −316/+28, −106/+28) (A3). (B) Ectopic expression of both zebrafish and human HSF1 or SP1 up-regulated the transcriptional activities of FOXM1 promoter, and Cu overload inhibited the increased transcriptional activities on human (B1, B2) and zebrafish (B3, B4) FOXM1 promoters, respectively. (C) Protein levels of SP1, MYC-SP1 (SP1), and MYC-HSF1 (HSF1) in Cu-stressed mammalian cells (C1). Reduced binding enrichment of protein SP1 (C2, C3) and HSF1 (C4) on FOXM1 promoter under Cu stresses as revealed by chromatin immunoprecipitation assays (ChIP). Anti-SP1 and Anti-MYC were used for ChIP assays in the control and the Cu-stressed cells, with anti-IgG used as the negative control. (D) Expression of HSF1 targeting genes BAX, SHC1, CDC6, CKS1B, and SP1 targeting genes CDC25A, MYCA in K562 cells. (E) The binding of the indicated proteins (HSF1/SP1) to Cu2+ and Fe3+ was assessed by western blot analysis of eluted proteins from the indicated metal-loaded resins. (F) Cu probe (Red+) and HSF1/SP1 protein (GFP+) double-positive foci were significantly increased in the cytoplasm of Cu overload K562 cells. F17, calculation of the number of Red+GFP+ foci in K562 cells from different groups. Data are mean ± SD. t-test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. NS, not significant. Scale bars, 2 μm (F1-F16). |