Figure 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230406-59
- Publication
- Li et al., 2023 - Copper overload impairs hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell proliferation via prompting HSF1/SP1 aggregation and the subsequently downregulating FOXM1-Cytoskeleton axis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
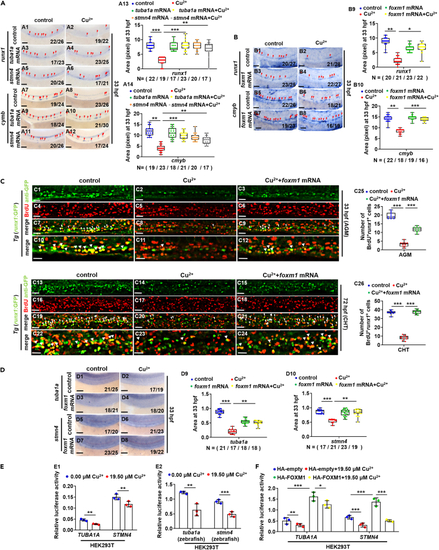
Ectopic expression of tuba1a, stmn4, or foxm1 could recover the proliferation of HSPCs in Cu-stressed embryos (A) Ectopic expression of tuba1a and stmn4 mRNA could recover the expression of runx1 or cmyb in Cu-stressed embryos at 33 hpf. A13, A14, calculation of gene expression in each embryo from different groups. (B) Ectopic expression of foxm1 mRNA could recover the expression of runx1 or cmyb in Cu-stressed embryos at 33 hpf. B9, B10, calculation of gene expression in each embryo from different groups. (C) Ectopic expression of foxm1 could recover BrdU cell proliferation in Cu-stressed embryos at 33 hpf (C1-C12) and 72 hpf (C13-C24). C25, C26, calculation of HSPC proliferation in embryos from different groups. (D) Ectopic expression of foxm1 mRNA could recover the expression of tuba1a and stmn4 in Cu-stressed embryos at 33 hpf. D9, D10, calculation of tuba1a and stmn4 expression in embryos from different groups. (E) Cu significantly suppressed the transcriptional activities of both human (E1) and zebrafish (E2) TUBA1A and STMN4 promoters. (F) Ectopic expression of human FOXM1 significantly up-regulated the transcriptional activities of TUBA1A and STMN4 promoter and Cu overload significantly suppressed the up-regulated transcriptional activities. A1-A12, B1-B8, C1-C24, D1-D8, lateral view, anterior to the left, and dorsal to the up. Data are mean ± SD. t-test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Scale bars, 20 μm (C1-C24) and 50 μm (A1-A12, B1-B8, D1-D8). |