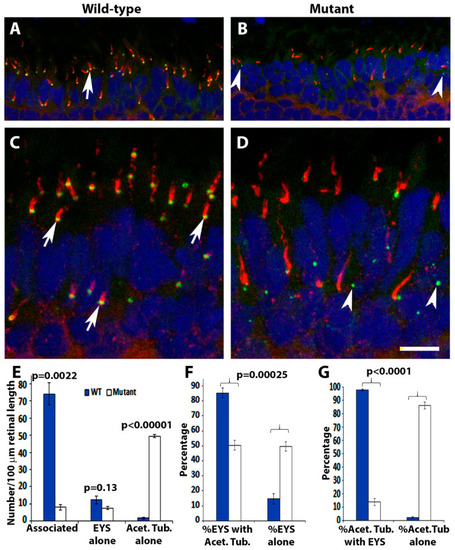
EYS protein was reduced and mis-localized in pomt2 mutant zebrafish retinas. Retinal sections from zebrafish at 1-mpf were double immunostained with EYS (green fluorescence) and acetylated α-tubulin (red fluorescence). The sections were counterstained with DAPI to show nuclei. (A,C) Wild-type retina at 1-mpf. Most EYS-positive puncta in the wild-type retina were associated with the basal end of acetylated α-tubulin reactivity (arrows). (B,D) pomt2sny5+13 homozygous mutant retina at 1-mpf. Overall, EYS immunoreactivity in the mutant was much lower than the wild-type. Most of the EYS-positive puncta were not associated with acetylated α-tubulin but were localized to the outer nuclear layer. (E) Counting of EYS-acetylated α-tubulin double staining from the outer nuclear layer to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) (n = 3). Note that acetylated α-tubulin reactivity associated with EYS puncta were decreased in the mutant, and acetylated α-tubulin not associated with EYS puncta were increased in the mutant. (F) Percentage of EYS associated with α-tubulin immunoreactivity and not associated with acetylated α-tubulin (n = 3). Note that EYS immunoreactivity associated with acetylated α-tubulin was reduced in pomt2 mutant retinas, but non-associated EYS puncta were increased in these animals. (G) Percentage of acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity associated and not associated with EYS (n = 3). Note that acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity associated with EYS was reduced but acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity not associated with EYS was increased in pomt2 mutant retinas. Scale bar in (D): 10.5 µm for (A,B); 5 µm for (C,D).
|

