Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221123-35
- Publication
- Sarvari et al., 2021 - The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Rbx1 regulates cardiac wall morphogenesis in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
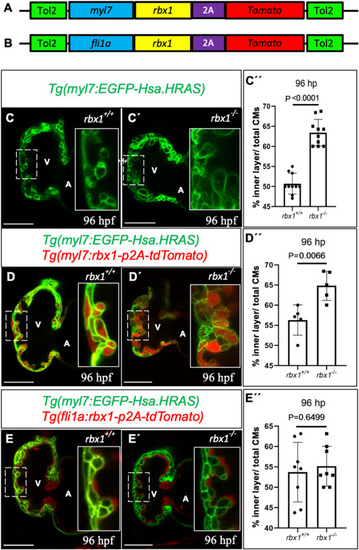
rbx1 overexpression in endothelial cells can rescue the multi-layered myocardial wall phenotype in rbx1 mutants (A-B) Cartoon of rbx1 overexpression transgene constructs under myocardial-specific (A) or endothelial-specific (B) promoters. (C?C?) Confocal images (mid-sagittal sections) of 96 hpf Tg(myl7:EGFP-Hsa.HRAS) rbx1+/+ (C) and rbx1?/? (C?) hearts. (D-E?) Overexpression of rbx1 in the endothelium but not the myocardium can rescue the myocardial wall phenotype in rbx1?/? larvae. (D-D?) Confocal images (mid-sagittal sections) of 96 hpf rbx1+/+ (D) and rbx1?/? (D?) hearts in the presence of the myl7:rbx1-p2a-tdTomato transgene. (E-E?) Confocal images (mid-sagittal sections) of 96 hpf rbx1+/+ (E) and rbx1?/? (E?) hearts in the presence of the fli1a:rbx1-p2a-tdTomato transgene. Magnified views of dashed areas shown in the right corners. (C"-E") Percentage of inner layer CMs relative to the total number of CMs comparing rbx1+/+ and rbx1?/? hearts having no rbx1 overexpression (C'?), and with overexpression of rbx1 in the myocardium (D'?) or endocardium (E'?). V: ventricle, A: atrium; scale bars, 50 ??m. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 480, Sarvari, P., Rasouli, S.J., Allanki, S., Stone, O.A., Sokol, A., Graumann, J., Stainier, D.Y.R., The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Rbx1 regulates cardiac wall morphogenesis in zebrafish, 1-12, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.