Fig 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221121-12
- Publication
- Sarmah et al., 2022 - Elf3 deficiency during zebrafish development alters extracellular matrix organization and disrupts tissue morphogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
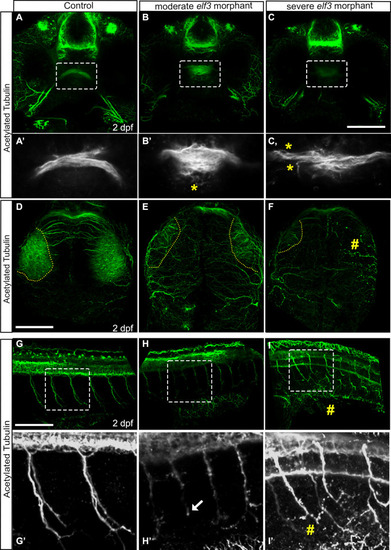
Elf3 deficiency caused optic nerve fasciculation and arborization in the optic tectum defects and fragmentation of spinal motor neurons.
(A-C) Confocal imaging of acetylated tubulin stained embryos and 3D rendering shows tightly fasciculated optic nerves crossing at the optic chiasm in the control embryo (A) and a smaller de-fasciculated nerve in the morphants (B, C). (A?-C?) High magnification of the marked rectangle area in A-C. yellow asterisk show fibers de-fasciculated. (D-F) Confocal imaging of acetylated tubulin stained embryos and 3D rendering shows optic nerves arborized extensively within the tectal neuropil in the control embryo (D), and either fewer or no axon projections within that region in the Elf3 morphants (E, F). yellow perforated lines: presumptive tectal neuropil region; #: no axon projections. (G-I) 3D renderings of the confocal sections of acetylated tubulin stained 2 dpf control embryos showed thick bundles of caudal motor neurons arborized within muscle in control embryo (G, G?) and fragmented, abnormally branched and shorter axons in the morphants (H, H?, I, I?). (G?-I?) High magnification of the marked rectangle area in G-I. Arrow: short axon; #: fragmented axon. Scale bar for A-C, D-F and G-I = 100 ?m. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |