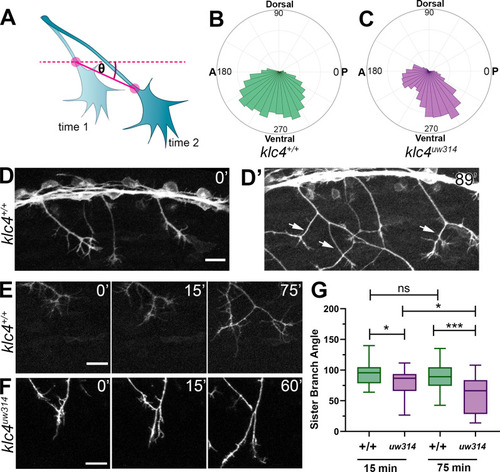
(A) Illustration of how axon growth direction was measured. The angle between an axon?s position in each frame and the frame preceding it was measured. (B?C) These angles were plotted as rose plots to show growth direction distributions. Wild type axons grow evenly between anterior and posterior directions, while klc4uw314 mutant axons show a preference for posterior directed growth. Wild type N=19 axons from 3 embryos. Klc4uw314 N=22 axons from 4 embryos. (D) Stills from a live capture of wild type axon outgrowth, showing that axons often grow posteriorly, but anterior directed branches form over time (D?, white arrows). (E) As a branch forms in a wild type peripheral axon, the angle between sister branches remains consistent as axons grow apart. (F) In klc4uw314 mutants, sister branches do not grow as far apart and the sister branch angle narrows over time compared to wild type. All scale bars = 20 Ám. (G) Quantification of the angle between newly formed sister branches at 15 and 75 min after branch creation. Wild type 15? N=37 branches, klc4uw314 15? N=36 branches, Wild type 75? N=25 branches, klc4uw314 75? N=18 branches. 4 embryos per genotype. *p=0.021, ***p=0.0003, One-way ANOVA. Error bars = 5-95th percentile.