|
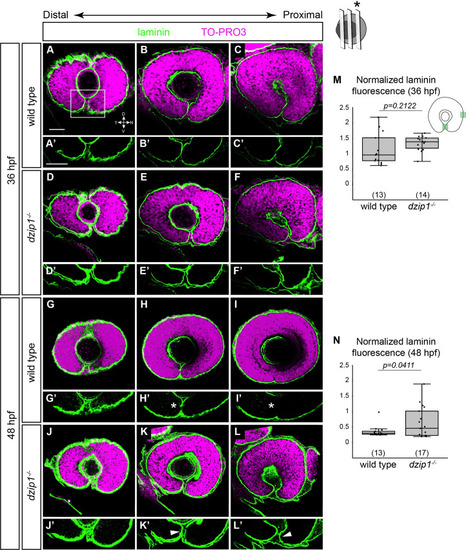
The optic fissure basement membrane fails to breakdown in <italic toggle='yes'>dzip1</italic> mutants.(A-L) Whole mount immunofluorescence for Laminin (green), and nuclei (magenta, TO-PRO-3) in wild type (A-C, G-I) and dzip1ts294e mutants (D-F, J-L) at 36 hpf (A-F), and 48 hpf (G-L). All images are lateral views. Single optical sections were obtained from three different depths along the proximal-distal axis of the eye (see Methods for details). (A’-L’) Insets of the optic fissure, the laminin channel alone (green) for wild type (A’-C’, G’-I’), and dzip1ts294e mutants (D’-F’, J’-L’), at 36 hpf (A’-F’) and 48 hpf (G’-I’). At 36 hpf, laminin protein completely lines the fissure in both genotypes. At 48 hpf, laminin protein is lost in the optic fissure in wild type embryos (H’, I’, white asterisks), whereas laminin continues to persist in the optic fissure in dzip1-/- embryos (K’, L’, white arrowheads). (M, N) Quantification of laminin fluorescence intensity in the optic fissure in the proximal optical section at 36 hpf and 48 hpf. Laminin fluorescence intensity at the optic fissure was normalized to the laminin fluorescence intensity at the nasal boundary of the eye next to the olfactory placode. n (embryos) for each genotype shown at the base of the graph. P-values were calculated using Welch’s t-test (M-O). Scale bar: 50 μm. D, dorsal; V, ventral; N, nasal; T, temporal.
|