Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220211-15
- Publication
- Wohlfart et al., 2022 - Accumulation of acetaldehyde in aldh2.1-/- zebrafish causes increased retinal angiogenesis and impaired glucose metabolism
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
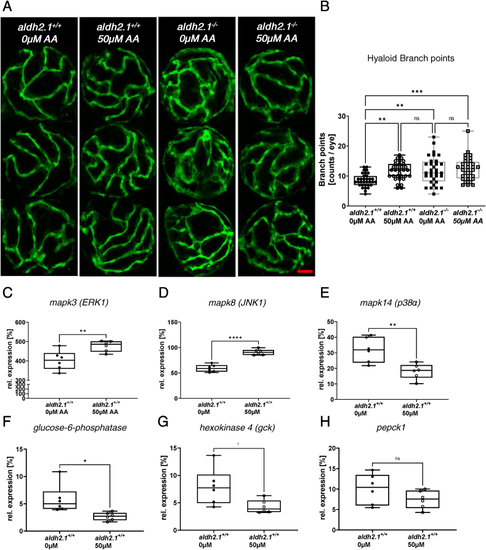
Exogenous AA caused angiogenic alterations in hyaloid vasculature, impairment of glucose metabolism and alteration of MAPK signaling. A: Representative confocal images of hyaloid vasculature in zebrafish larvae at 120 hpf with and without AA treatment. Red scale bar: 20 ?m. B: Quantification of larval hyaloid vasculature showed increased numbers of branch points in aldh2.1+/+ larvae after AA (50 ?m) treatment, which was not further enhanced in aldh2.1?/? larvae, n = 32?33 eyes per group. C-E: Expression of MAPK family members. ERK1 gene expression (C) was increased in aldh2.1+/+ larvae after AA treatment. Additionally, aldh2.1+/+ larvae with 50 ?m AA treatment exhibited increased JNK1 expression (D) and decreased p38? expression (E). F?H: Expression of selected genes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Reduced expression of g6pc (F) and gck (G) after AA treatment. pepck gene expression (H) was also reduced, although not significantly. Expression was quantified via RT-qPCR with 96 hpf zebrafish larvae and normalized to arnt2, n = 6 clutches, 50 larvae per clutch. Statistical analysis was done via Student's t-test, ns = not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |