|
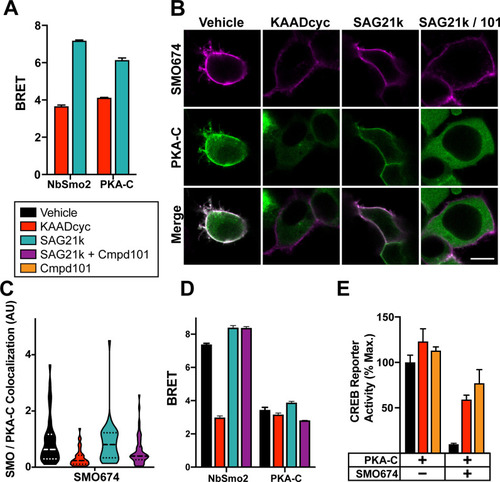
SMO/PKA-C interactions depend on SMO and GRK2/3 activity.(A) HEK293 cells transfected with SMO657-nanoluc and PKA-C-YFP were treated with SMO inverse agonist KAADcyc (1 μM) or agonist SAG21k (1 μM) for 1 hour prior to BRET measurements. (B) Images of HEK293 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged SMO674 (magenta) and YFP-tagged PKA-C (green) and treated with vehicle, KAADcyc (300 nM), or SAG21k (100 nM) alone or with the GRK2/3 inhibitor Cmpd101 (“101”, 30 μM). Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Quantification of colocalization between SMO and PKA-C for the experiment in (B) (see “Methods’). (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with SMO657-nanoluc and YFP-tagged versions of either NbSmo2 or PKA-C and treated with vehicle, KAADcyc (1 μM), or SAG21k (1 μM) for 1 hour or with Cmpd101 (30 μM) for 4 hours. (E) Effect of KAADcyc (1 μM) or Cmpd101 (30 μM) on SMO inhibition of the CREB reporter in HEK293 cells. For (E), CREB reporter was normalized to 100%, which reflects reporter activation from PKA-C-transfected cells treated with vehicle. Data in (A), (D), and (E): n = 3–6 biological replicates per condition. Error bars = SEM. Data in (C): n = 119–216 cells per condition pooled from 2 or more independent experiments. The underlying data for this figure can be found under S5 Data. See S1 Table for statistical analysis. BRET, bioluminescence resonance energy transfer; GRK, GPCR kinase; Cmpd101, Compound 101; CREB, cyclic AMP response element binding protein; KAADcyc, KAAD-cyclopamine; PKA-C, PKA catalytic subunits; SMO, Smoothened.
|