|
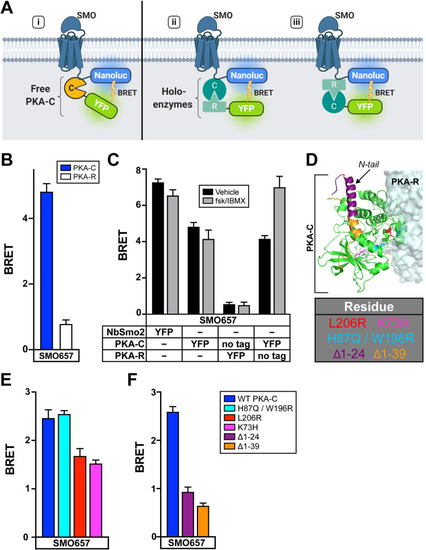
SMO interacts with free PKA-C subunits rather than PKA holoenzymes.(A) Schematic of BRET assays to test whether SMO interacts with (i) free PKA-C or intact PKA holoenzymes via (ii) PKA-C or (iii) PKA-R subunits. (B) BRET between an SMO657-nanoluc donor and YFP-tagged PKA-C or PKA-R in HEK293 cells. (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with an SMO657-nanoluc donor and untagged or YFP-tagged PKA-C or PKA-R subunits, as described in the table. To stimulate cAMP production, cells were treated for 4 hours with forskolin (10 μM) + the phosphodiesterase inhibitor IBMX (1 mM), which blocks cAMP degradation, prior to BRET measurements. (D) Structure of PKA holoenzyme (PDB: 4X6R). Key PKA-C residues are colored in the structure and indicated in the table (below). (E) BRET between SMO and PKA-C harboring mutations in various regions of the PKA-R binding interface (H87Q/W196R or L206R) or the active site (K73H). (F) BRET between SMO and PKA-C harboring deletions of the first 24, or all 39, amino acids from the N-tail. Data are reported as BRET ratios and background-subtracted as in Fig 3 (n = 3–6 biological replicates per condition; error bars = SEM). The underlying data for this figure can be found under S4 Data. See S1 Table for statistical analysis. BRET, bioluminescence resonance energy transfer; cAMP, cyclic AMP; IBMX, isobutylmethylxanthine; PKA, protein kinase A; PKA-C, PKA catalytic subunits; PKA-R, PKA regulatory subunits; SMO, Smoothened; WT, wild-type.
|