|
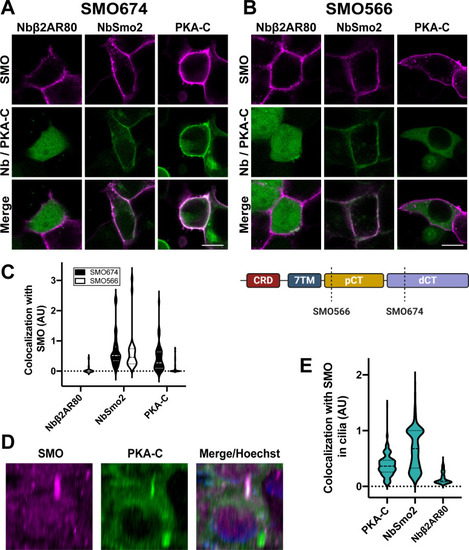
SMO uses its essential pCT domain to recruit PKA-C to the membrane.HEK293 cells expressing (A) FLAG-tagged SMO674 that contains the pCT or (B) FLAG-tagged SMO566 that lacks the pCT (see cartoon at lower right) were cotransfected with Nbβ2AR80-GFP, NbSmo2-YFP, or PKA-C-YFP. Confocal microscopy images show SMO (magenta) and co-expressed proteins (green). Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Quantification of colocalization for studies in (A) and (B). (n = 29–121 cells per condition). Note that Nbβ2AR80 displayed a background-subtracted colocalization index of “0” in all SMO674-expressing cells examined. (D) Three-dimensional reconstruction of IMCD3 cells stably coexpressing FLAG-tagged SMO (magenta) with mNeonGreen-tagged PKA-C (green). After treatment with SAG21k to induce SMO accumulation in cilia, live cells were stained with anti-FLAG antibodies (magenta) and Hoechst (blue), then examined via confocal microscopy. See S3 Fig for images from cells expressing FLAG-tagged SMO with mNeonGreen-tagged NbSmo2 or Nbβ2AR80. (E) Quantification of colocalization between SMO and PKA-C, NbSmo2, or Nbβ2AR80 for the experiment described in (D) (n = 197–236 cilia per condition). The underlying data for this figure can be found under S2 Data. dCT, distal segment of the cytoplasmic tail; pCT, proximal segment of the cytoplasmic tail; PKA-C, PKA catalytic subunits; SMO, Smoothened.
|