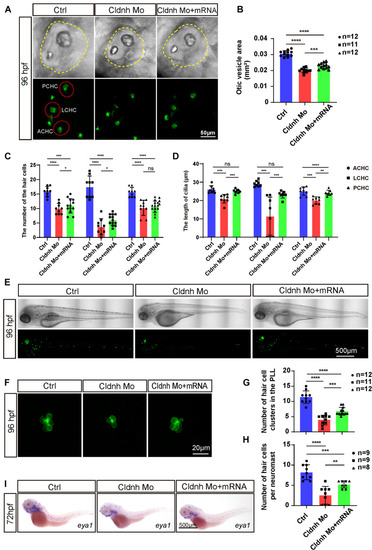
Overexpression of claudin h could rescue the development defects of hair cells in claudin morphants. (A) Imaging analysis of otic vesicle and cristae hair cells in control, claudin h morphants, and rescue group at 96 hpf. The yellow dotted line marked the boundary of the otic vesicle. Scale bar = 50 mm. (B,C) The statistical analysis of otic vesicle area in different groups at 96 hpf. (C,D) The statistical analysis of the number of different cristae hair cells and the cilia lengths in different groups at 96 hpf. (E) WISH results of the eya1 gene and the imaging analysis of control, claudin h morphants and rescue zebrafish at 96 hpf in bright field and fluorescent field. Scale bar = 500 μm. (F) Quantification of the number of hair cell clusters in the posterior lateral line of different groups at 96 hpf. (G) Confocal imaging analysis of L1 hair cell clusters in the posterior lateral line of different groups at 96 hpf. (H) Quantification of the number of hair cells per L1 neuromast in the control, claudin h morphants, and rescue zebrafish at 96 hpf. Values with *, **, ***, and ****above the bars are significantly different (P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001, and P < 0.0001, respectively). (I) At 72 hpf, the in situ hybridization signal of claudin h in the control zebrafish, claudin h morphants, and rescue zebrafish.
|

