Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210405-23
- Publication
- Farrugia et al., 2020 - Mechanisms of vascular damage by systemic dissemination of the oral pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
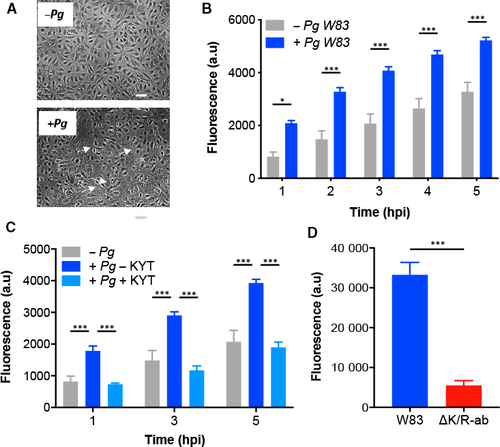
Pg W83 increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers in a gingipain?dependent manner. HDMEC (A?C) or HMEC?1 (D) cells were grown to confluent monolayers on fibronectin?coated inserts, infected with Pg at a MOI 1000 for 1.5 h, followed by the measurement of high molecular weight (70 kDa) fluorescein dextran passing through the monolayer barrier. Morphology of HDMEC monolayer in the absence (?Pg) or presence (+Pg) of W83 (A); white arrows indicate areas of cell attachment loss (scale bar in A = 20 ?m). In vitro permeability assay of HDMEC in the absence (?Pg) or presence (+Pg) of W83 (B) and upon treatment with KYT inhibitors prior to HDMEC Pg infection (C). In vitro permeability assay of HMEC?1 infected with W83 or ?K/R?ab (D). Data in B&C are presented as means ± SD and were analysed by one?way ANOVA followed by Tukey?s post hoc comparison test. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Data in D are presented as means ± SD and were analysed by Student's t?test. ***P < 0.001; for all experiments, n = 3 individual experiments with each individual experiment performed in triplicate technical repeats. |