|
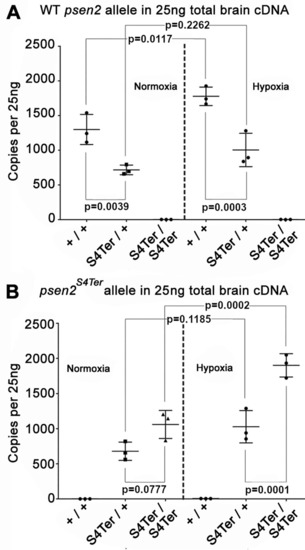
Allele-specific mRNA expression in the brains of 6-month-old fish of different genotypes under normoxia or acute hypoxia (as copies per 25 ng of brain cDNA in each dqPCR).(A) The levels of wild type psen2 allele mRNA in the psen2S4Ter/+ fish (~700 copies) were significantly (p = 0.0039) lower than in their wild type siblings (~1,300 copies) under normoxia. Under hypoxia, the levels of wild type psen2 allele mRNA in both the psen2S4Ter/+ fish (~1,000 copies) and their wild type siblings (~1,800 copies) were apparently up-regulated, but only the higher levels in the wild type fish showed a statistically significant increase (p = 0.0117) compared to the normoxic controls. (B) The levels of psen2S4Ter allele mRNA in the psen2S4Ter/+ fish (~700 copies) appeared to be lower than in the psen2S4Ter/psen2S4Ter fish (~1,000 copies) under normoxia. However, this comparison did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.0777). Under hypoxia, the levels of psen2S4Ter allele mRNA in both the psen2S4Ter/+ fish (~1,000 copies) and the psen2S4Ter/psen2S4Ter fish (~1,900 copies) were upregulated. This up-regulation in the psen2S4Ter/psen2S4Ter fish was clearly significant (p = 0.0002), while that in the psen2S4Ter/+ fish was apparent, but not regarded as statistically significant (p = 0.1185). Data is shown as the mean ± SD. Values of p were determined by a two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test. The dqPCR raw data is given in S1 & S2 Tables in S1 File.
|