Fig. 4
|
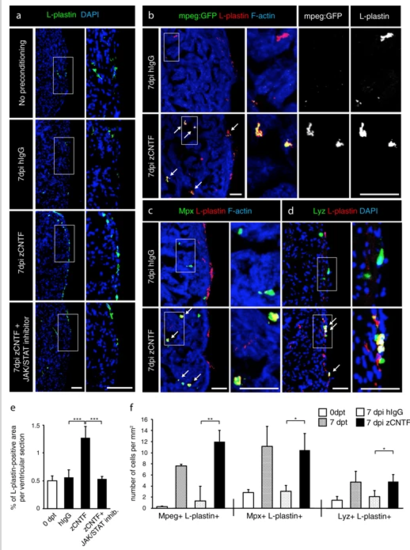
Exogenous zCNTF recruits leucocytes into the zebrafish uninjured heart. a–dImmunofluorescence staining of heart sections from different conditions as indicated at the left side of the images. a Hearts of wild type fish stained for L-plastin (green) and DAPI (blue). Single injection of zCNTF results in higher accumulation of L-plastin in the heart at 7 dpi. This effect is abolished in the presence of the JAK/STAT inhibitor, 1 µM Ruxolitinib. Scale bars, 100 μm. b Hearts of transgenic fish mpeg1:EGFP (green) stained for L-plastin (red) and F-actin (Phalloidin, blue). The number of mpeg1:EGFP/L-plastin-expressing cells is increased at 7 days after zCNTF injection. Some double positive cells are indicated with arrows. Scale bers 50 μm. c, d Ventricles of wild type fish stained for Mpx (c, green) or Lyz (d; green) and F-actin (Phalloidin, blue). The number of double positive leucocytes is increased at 7 days after zCNTF injection (arrows). Scale bars, 50 μm. e Quantification of L-plastin + area in ventricular sections. f Quantification of cells expressing mpeg1:EGFP, Mpx and Lyz normalized to the ventricle area at different conditions. n ≥ 4 hearts; ≥ 2 sections per heart; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 |