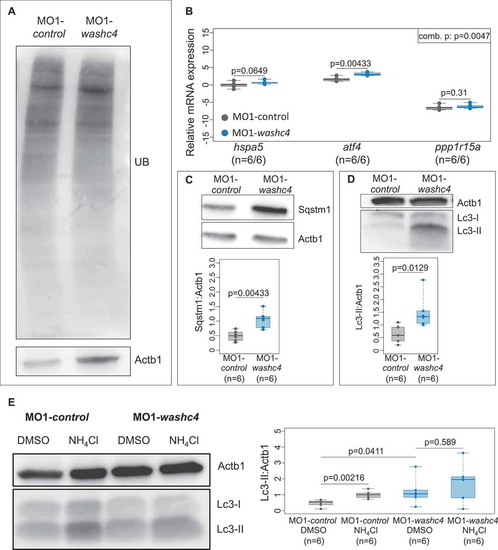
Loss of Washc4 leads to an upregulation of ER stress markers and to an impaired autophagy. (a) Western blot analysis of ubiquitinated proteins after MO1-control and MO1-washc4 injection. (b) qRT-PCR of ER stress markers (hspa5, atf4 and ppp1r15a) of control embryos or washc4 morphants at 3 dpf. The individual measurements are shown (log10). The 3 markers were analyzed via Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. A combined P value (comb. p) was determined via a modified Fisher method. slc25a5 was used as housekeeping gene. (c) Western blot analysis using anti-Sqstm1 antibody after MO1-control and MO1-washc4 injection (upper panel); quantification of gray values (lower panel; n = 6). (d) Representative western blotting of Lc3 of control embryos or washc4 morphants (upper panel); quantification of gray values (lower panel; n = 6). Individual measurements are shown (Wilcoxon rank-sum test). (e) MO1-control-or MO1-washc4-injected embryos treated with DMSO or ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). Control embryos show a significant increase of Lc3-II levels after NH4Cl treatment in comparison to DMSO controls. Ammonium chloride treatment of Washc4 morphants did not significantly enhance the Lc3-II level in comparison to DMSO treated embryos (n = 6). Actb1/β-actin was used as loading control. The individual measurements are shown (Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
|

