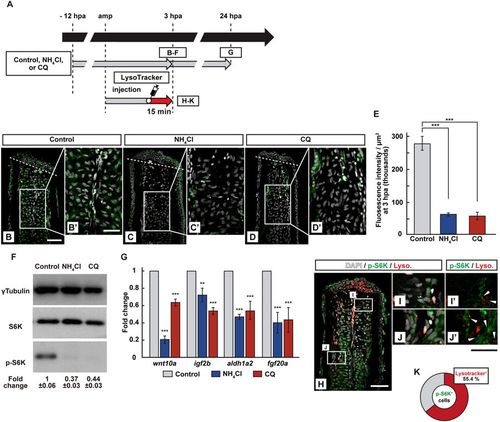
Requirement of lysosomal acidification in the S6K activation. (A) Experimental scheme. NH4Cl or chloroquine (CQ) was treated from ?12 to 3 or 24 hpa (B?G). LysoTracker solution was injected into the amputated fins 15?min before fixation (H?K). (B?E) Longitudinal ray sections and quantification of p-S6K fluorescence intensities per area that consist of the whole regenerates and 500??m below the amputation plane in control, NH4Cl-, or CQ-treated fin stumps at 3 hpa; p-S6K and nuclei were visualized by immunohistochemical staining and DAPI staining, respectively (n?=?5). Representative images (B?D?) used for quantification are shown in (E). White dashed lines indicate the amputation planes. Scale bars: 50??m (B?D) and 25??m (B??D?). ***p?<?0.001 by Student?s t test. Error bars represent the standard error. (F) Western blotting analysis of ?Tubulin, S6K, and p-S6K in the DMSO-, NH4Cl-, or CQ-treated fin stumps at 3 hpa. ?Tubulin serves as a loading control. Numbers below each lane show the level of p-S6K in NH4Cl-, or CQ-treated fin stumps relative to that in DMSO-treated fin stumps at 3 hpa normalized to loading control. (G) The relative expression of growth factor-related genes in NH4Cl- or CQ-treated fin stumps by qPCR at 24 hpa. ***p?<?0.001, **p?<?0.05 by Student?s t test. Error bars represent the standard error. (H?K) Longitudinal ray sections and quantification of p-S6K+ and LysoTracker fluorescence+ cells in area that consist of the whole regenerates and 500??m below the amputation plane at 3 hpa; p-S6K (green), nuclei (grayscale), and lysosomal acidification (red) were visualized by immunohistochemical staining, DAPI, and LysoTracker (Lyso.), respectively (n?=?8). White boxed areas in (H) are enlarged in (I?J?), respectively. Representative images (H?J?) used for quantification are shown in (K). Arrowheads in (I? and J?) indicate LysoTracker fluorescence and p-S6K double positive cells. Scale bars: 50??m (H) and 25??m (I?J?). A pie chart shows that 55.4% of p-S6K+ cells are the LysoTracker fluorescence positive cells (K).
|

