Fig. 5
|
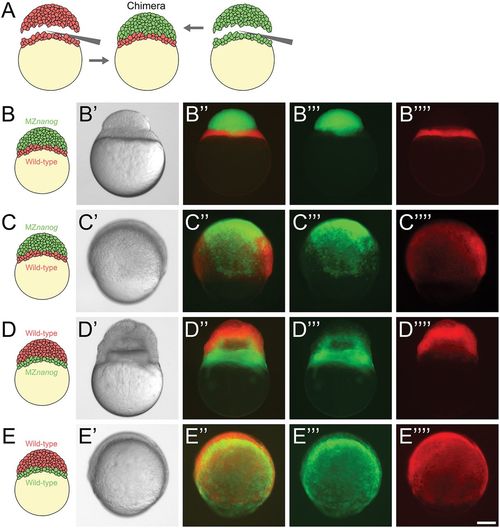
Blastoderm transplants between wild-type and MZnanog embryos. (A) Diagram of the blastoderm transplant. Donor embryos were injected with dextran-Alexa-488 or dextran-Alexa-546. Blastoderms were separated from yolks and combined to generate chimera embryos. (B) A chimera imaged approximately 15?min after transplant of a wild-type yolk cell and YSL with MZnanog blastoderm (B-B??), where MZnanog tissue is labeled in green (B?) and wild-type tissue is labeled in red (B??). (C) A chimera at 8?hpf of a wild-type yolk cell and YSL with MZnanog blastoderm (C-C??), where MZnanog tissue is labeled in green (C?) and wild-type tissue is labeled in red (C??). (D) A reciprocal chimera at 8?hpf of wild-type blastoderm with MZnanog yolk cell (D-D??), again with MZnanog tissue labeled in green (D?) and wild-type tissue labeled in red (D??). (E) A chimera at 8?hpf of a wild-type yolk cell and YSL with a wild-type blastoderm from a second embryo (E-E??), where tissue derived from each donor embryo is distinctly labeled (E?,E??). Composites of the fluorescent channels are shown in B?, C?, D? and E?. Scale bar: 100??m. |