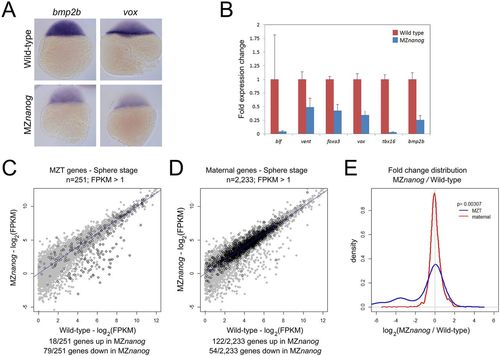
Defects in early zygotic gene expression in MZnanog embryos. (A) In situ hybridization for bmp2b and vox expression in wild-type and MZnanog embryos at sphere (4?hpf) stage. (B) Fold expression change for the indicated genes comparing wild type and MZnanog at sphere stage using RT-qPCR. Error bars show s.d. for three technical replicates (ten embryos per replicate). (C) Differential expression of early zygotic genes, comparing wild type and MZnanog at sphere stage using RNAseq. All genes are in gray, early zygotic genes (MZT genes) in black were previously defined (Lee et al., 2013). (D) Differential expression of maternally provided genes, comparing wild type and MZnanog at sphere stage using RNAseq. All genes are in gray, maternally provided genes in black were previously defined (Rabani et al., 2014). Only those genes with wild-type mRNA expression >1 FPKM are plotted. Genes are categorized as up- or downregulated if their expression in MZnanog differs more than 2-fold from that in wild type. (E) Distribution of fold changes between wild-type and MZnanog embryos for all early zygotic (blue) and maternal (red) genes visualized using a kernel density estimation. The displayed P-value comparing these two sets was calculated using a Student's two-tailed t-test.
|

