Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170607-19
- Publication
- Benedetti et al., 2016 - INaP selective inhibition reverts precocious inter- and motorneurons hyperexcitability in the Sod1-G93R zebrafish ALS model
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
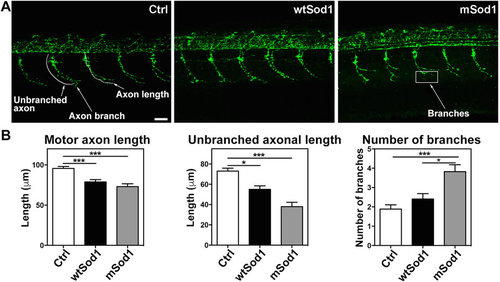
Sod1 overexpression causes motor nerve alterations at 24 hpf. (A) Confocal fluorescence maximum projection images showing SV2A signals (green) in the 12?16th somite region of the entire trunk of control (Ctrl), wtSod1 and mSod1 zebrafish embryos at 24?hpf (the same analysis was made in the 17?21st somite region with comparable results, data not shown). As synaptic vesicles travel the entire axonal length, it is possible to observe the length of embryonal motor axons and motor nerve branches. Scale bar: 25??m. (B) Both wtSod1 (78.9?±?2.8??m) and mSod1 embryos (73.1?±?3.5??m) showed significantly shorter motor axons than the Ctrl (95.6?±?2.4??m) and a significant decrease in unbranched axonal length (55.0?±?3.5 and 38.0?±?4.3??m vs 73.0?±?2.8??m), but only the mSod1 embryos showed a significant increase in the number of motor nerve branches: 3.8?±?0.4 vs 1.9?±?0.2 (Ctrl) and 2.4?±?0.3 (wtSod1). The columns indicate the mean value?±?SEM of the indicated parameter in at least five motor nerves of each of 25 Ctrl, 17 wtSod1, and 21 mSod1 embryos. The measures were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test, respectively corrected by means of Tukey?s or Dunn?s multiple comparison test (*P?<?0.05; ***P?<?0.001). |
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |