Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-161122-42
- Publication
- Mouti et al., 2016 - Minimal contribution of ERK1/2-MAPK signalling towards the maintenance of oncogenic GNAQQ209P-driven uveal melanomas in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
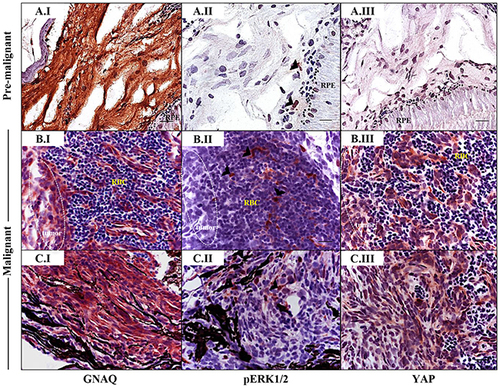
Sporadic ERK activation contrasted with ubiquitous nuclear YAP in malignancies in Tg (mitfa:GNAQQ209P;p53M214K/M214K) zebrafish. Sections of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded zebrafish eye specimens were stained for GNAQ, pERK1/2, and YAP by IHC, visualized by ImmPact NovaRed peroxidase (HRP) substrate then counterstained with hematoxylin (purple nuclei). A.I-A.III. Representative IHC images of benign hyperproliferative choroid. (A.I) Uniform expression of GNAQ in hyperplastic choroidal melanocytes. (A.II) Only a few cells (black arrowheads) are immunoreactive to pERK1/2. (A.III) Comparatively, more cells displayed nuclear YAP (brown nuclei), although again, this was more noticeable for cells residing at the interface. B.I-B.III; C.I-C.III. Representative IHC images of malignant choroidal melanocytes in two independent GNAQQ209P-driven uveal tumours. (B.I, C.I) Transformed melanocytes expressing GNAQ. (B.II, C.II) Malignant cells showing only sporadic immunoreactivity to pERK1/2 (cells showing positive immunoreactivity are indicated with black arrowheads). (B.III, C.III) Ubiquitous YAP nuclear localization (brown nuclei) in transformed uveal melanocytes. Images are representative of sections from three animals. Abbreviations: RPE, retinal pigmented epithelium; RBC, red blood cells. Scale bars, 20 ?m. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Days 45-89 to Adult |