Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140114-60
- Publication
- Leigh et al., 2013 - Mmp17b is essential for proper neural crest cell migration in vivo
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
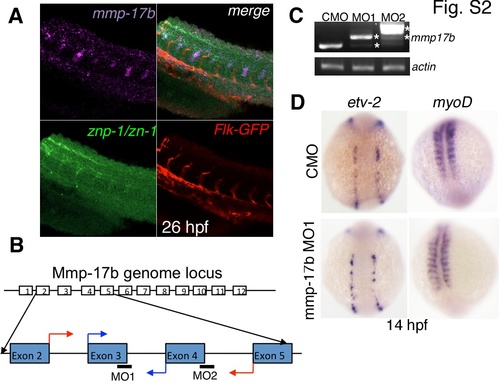
mmp17b expression, knockdown efficacy and role in early development. A shows three color staining of the trunk of a 26 hpf embryo for motor neurons. Upper left panel is mmp17b in purple, lower left panel is znp-1/zn-1 motor neuron staining in green, lower right panel is Flk-GFP staining endothelial cells in red, and the upper right panel is a merge. The upper right panel shows co-localization of mmp17b and znp-1/zn-1 staining. B shows cartoon illustrating where the mmp17b morpholinos (MO) were targeted. MO1 and MO2 targeted the exon-intron boundary of exons 3 and 4 respectively. Blue arrows indicate start of primers used to confirm efficacy of MO1. Red arrows indicate start of primers used to confirm efficacy of MO2. C shows efficacy for MO1 and MO2 demonstrated via RT-PCR. Primers illustrated in panel B were used to amplify mmp17b fragments. In both MO1 and MO2, the mmp17b amplicon was larger than the control MO injected sample. In MO1, there appeared to be a major higher band along with a minor band that was consistent with the normal mmp17b band. In MO2, there was a major band much higher than control and a minor band consistent with the higher band observed in the MO1 sample. Asterisks indicate the aberrant transcripts. β-actin was used as a loading control. D shows knockdown of mmp17b does not affect early development. When etv-2 (upper and lower left panels) and myoD (upper and lower right panels) are probed for in 14 hpf mmp17b MO1 injected embryos (lower left and right panels), there is no difference observed compared to control MO injected embryos (upper left and right panels). |