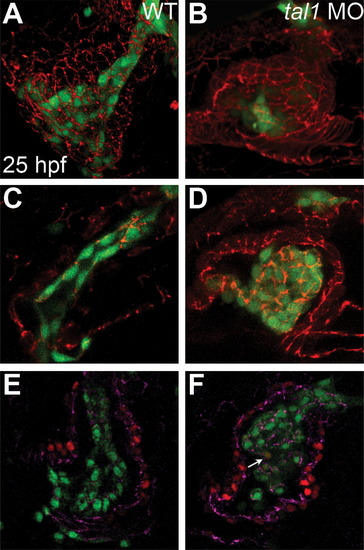
Endocardial intercellular junctions are disorganized following heart tube extension in tal1-deficient embryos. (A?D) Immunofluorescence detects localization of ZO-1 (red) in wild-type (A and C) and tal1-deficient (B and D) hearts at 25 hpf; lateral views, ventricular end of the heart tube at the top. An anti-GFP antibody allows visualization of Tg(kdrl:GRCFP) expression (green) in the endocardium. (A and B) Three-dimensional reconstructions of confocal stacks demonstrate that ZO-1 is located around the perimeter of the myocardial cells in both wild-type and tal1-deficient hearts. (C) Optical slice of a wild-type heart reveals that ZO-1 is localized in discrete puncta at points of endocardial cell-cell contact; in addition, wild-type endocardial cells exhibit a flattened and elongated morphology. (D) Optical slice of a tal1-deficient heart reveals that ZO-1 is mislocalized in large clusters around the perimeter of the endocardial cells; in addition, the tal1-deficient endocardial cells exhibit a rounded shape, rather than the normal elongated shape. (E and F) Immunofluorescence detects ZO-1 (purple) in wild-type (E) and tal1-deficient (F) hearts at 25 hpf; lateral views, ventricular end of the heart tube at the top. Expression of the Tg(fli1a:negfp) (green) and Tg(myl7:H2A-mCherry) (red) transgenes reveals one endocardial cell with ectopic myocardial gene expression (arrow). Subcellular localization of ZO-1 is aberrant in the majority of tal1-deficient endocardial cells, nearly all of which do not display ectopic myocardial gene expression.
|

