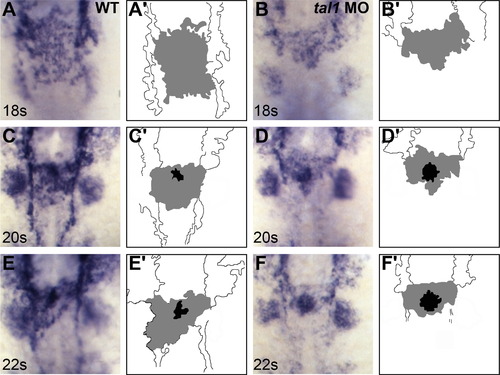
Defects in endocardial sheet formation appear after tal1-deficient endocardial cells arrive at the midline. (A?F) Dorsal views of wild-type (A, C, and E) and tal1-deficient embryos (B, D, and F), anterior to the top, displaying the expression of fli1a at the 18 somite (18s) (A and B), 20s (C and D), and 22s (E and F) stages. (A′?F′) Cartoons indicate regions of fli1a expression in the endocardium (gray and black) and cranial endothelium (white). fli1a expression in the branchial arches is visible in the images (A?F) but is not indicated in the cartoons (A′?F′). (A, C, and E) In wild-type embryos, an endocardial sheet spreads along the anterior-posterior axis by 18s (A). Increased expression of fli1a becomes apparent at the future apex (black areas in C′ and E′) of the endocardial tube as the endocardial sheet transforms into a tube extending toward the left side of the embryo (C and E). (B, D, and F) In tal1-deficient embryos, the expression of fli1a is maintained normally, consistent with previous reports (Patterson et al., 2005). Instead of spreading out into a sheet, the tal1-deficient endocardial cells aggregate at the midline (B) and subsequently fail to migrate toward the left (D and F).
|

