Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130822-37
- Publication
- Sah et al., 2013 - Ion channel-kinase TRPM7 is required for maintaining cardiac automaticity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
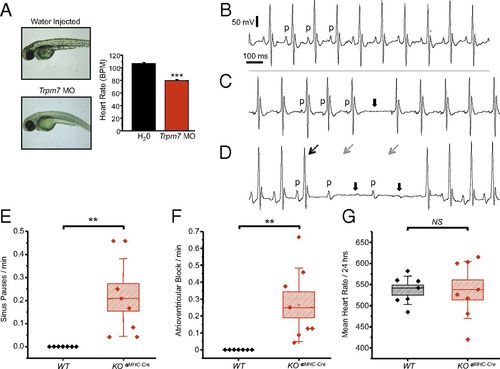
Trpm7 deletion in vivo disrupts automaticity in zebrafish and induces SPs and AVB in mice. (A) (Left) Images of zebrafish embryos: water-injected (Upper) and Trpm7 MO-injected (Lower). (Right) Trpm7 MO zebrafish (n = 30) and water-injected zebrafish (n = 27) heart rates. (B) Normal sinus rhythm (p denotes P waves; atrial depolarization) with intact atrioventricular conduction in the ECG of a telemetered, conscious WT mouse. (C) Representative ECG showing an episode of SP observed in a KOαMHC-Cre mouse. Solid arrows denote location of expected p waves. (D) Representative ECGs demonstrating AVB observed in KOαMHC-Cre mice (broken black arrow, conducted QRS complexes; broken gray arrow, expected location of QRS complex). (E and F) Box plots with overlying data points showing the distribution of the frequency of (E) SPs and (F) AVB observed over 24 h of telemetric monitoring in WT (n = 7) and KOαMHC-Cre (n = 8) mice. (G) Mean heart rates of WT and KOαMHC-Cre over a 24-h period were not statistically different. In box plots, error bars represent the SD of the mean. Box height represents the SE. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |