Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-121031-38
- Publication
- Shimizu et al., 2012 - Visualization and exploration of Tcf/Lef function using a highly responsive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-reporter transgenic zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
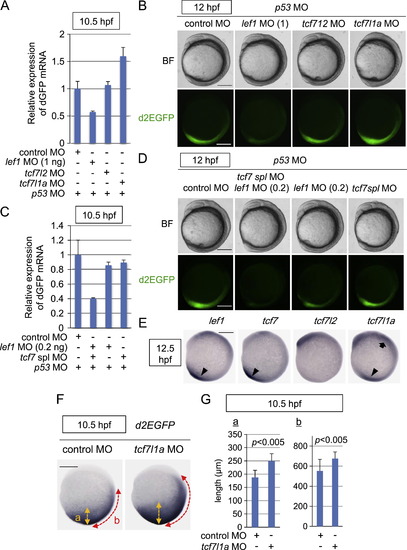
Tcf/Lef-miniP:dGFP reporter activity during early embryogenesis was dependent on the Tcf/Lef family of transcription factors. (A?D) The Tcf/Lef-miniP:dGFP reporter activity was regulated positively by Lef1, Tcf7, and Tcf7l2 and negatively by Tcf7l1a. Control MO, 1 or 0.2 ng of lef1 MO, tcf7l2 MO, tcf7l1a MO, or tcf7 spl MO was coinjected with p53 MO into one cell-stage Line-2 embryos, as indicated. (A, C) At 10.5 hpf, 20 embryos were collected and their total RNA was purified. The relative expression levels of d2EGFP mRNAs at 10.5 hpf were analyzed by qPCR. (B, D) Left-side views of MO-injected reporter fish embryos, as indicated, with the anterior side to the top. Scale bar, 200 μm. (E) Whole-mount in situ hybridization staining for lef1, tcf7, tcf7l2, and tcf7l1a in 12.5-hpf zebrafish embryos. Tcf/Lef mRNA expression in the anterior and posterior tissues is indicated with arrows and arrowheads, respectively. Scale bar, 200 μm. (F, G) Tcf7l1a negatively regulated Tcf/Lef-miniP:dGFP reporter activity. Control MO (n=28) or tcf7l1a MO (n=38) was coinjected with p53 MO into one cell-stage Line-2 embryos as indicated. (F) Whole-mount in situ hybridization staining for d2EGFP using 10.5-hpf MO-injected Line-2 embryos. Scale bar, 200 μm. (G) The width of the d2EGFP mRNA-expressing area was quantified by measuring the lengths of ?a? and ?b?, which are indicated in (F), using Image J (NIH). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 370(1), Shimizu, N., Kawakami, K., and Ishitani, T., Visualization and exploration of Tcf/Lef function using a highly responsive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-reporter transgenic zebrafish, 71-85, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.