Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120126-4
- Publication
- Peukert et al., 2011 - Lhx2 and lhx9 determine neuronal differentiation and compartition in the caudal forebrain by regulating wnt signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
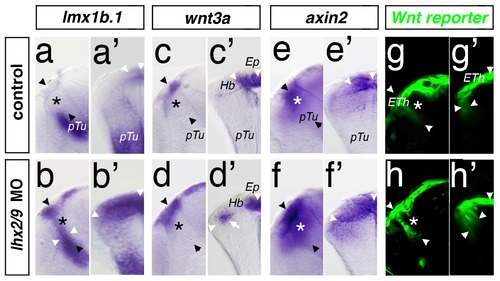
Knock-down of Lhx2/Lhx9 leads to an expansion of the Wnt positive epithalamus. A lateral view (a, b, c, etc.) and a cross-section (a2, b2, c2, etc.) of the left hemisphere of the same embryo at 48 hpf are displayed. Thalamus is marked by asterisks. Section plane of the cross-section is indicated by black arrowheads. In control MO injected embryos, lmx1b.1 expression domain marks the MDO and the dorsal RP (a, a2). Knock-down of Lhx2/Lhx9 leads to an expansion of both areas into the thalamic territory (b, b2). wnt3a marks the epiphysis but not the habenula territory (c, c2). In Lhx2/Lhx9-deficient embryos, wnt3a expression is ectopically activated in the dorsal part of the thalamus (d, d2). Subsequently the expression of Wnt target genes such as axin2 (e, e2) as well as the Wnt reporter line 7×TCF-Xla Siam:GFP ia4 (g, g2) shows an expanded expression domain in compound morphant embryos (f, f2 and h, h2). Ep, epiphysis; Hb, habenula; pTu, posterior tuberculum. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |