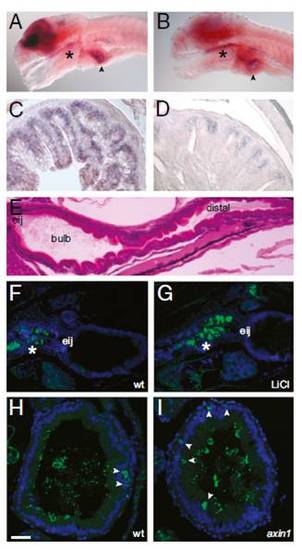
Wnt signaling occurs in the larval zebrafish intestine. (A) In situ hybridization with a tcf4 probe reveals strong brain expression as well as signal in the pharynx (*) and intestinal bulb (arrowhead) in a 6-dpf larva. (B) In situ hybridization with a sox9b probe reveals expression in the brain, pharynx (*), and intestinal bulb (arrowhead) of a 6-dpf larva. Sections of adult proximal intestine displaying expression of tcf4 (C) and sox9b (D) are shown. (E) H&E sagittal section of a 5-dpf larva showing the location of the esophageal intestinal junction (eij), bulb, and distal intestine. Sagittal sections of 6-dpf untreated (F) and LiCl-treated (G) larvae show β-catenin expression (green) in the pharynx and esophagus (*). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Transverse sections through the intestinal bulb of 6-dpf WT (wt) (H) and axin1 mutant (I) larvae show scattered cells with cytoplasmic β-catenin staining (green, arrowheads). Luminal microbes cross-react with the anti-β-catenin antisera. Nuclei are stained with Torpo (blue). (Scale bars: A and B, 100 μM; C and D, 25 μM; E?G, 50 μM; H and I, 15 μM.)
|

