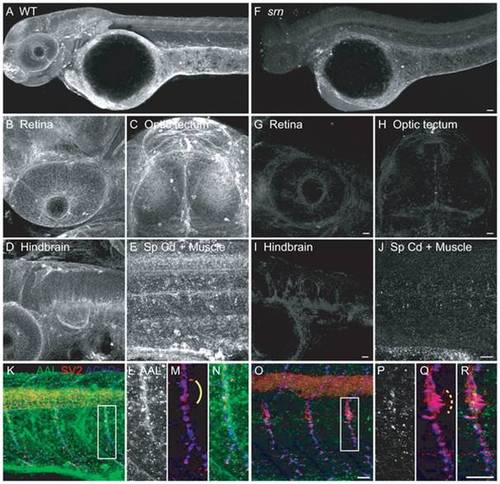
A. AAL staining of WT embryos at 48 hpf showed that protein fucosylation is present throughout the embryo (10?15 embryos/2?3 adult pairs for all analyses). B?E. Protein fucosylation is prominent in several neural tissues including retina (lateral view), optic tectum (dorsal view), hindbrain (lateral view), spinal cord (lateral view) and neuromuscular synapses (lateral view of axial muscle). F. Protein fucosylation is dramatically reduced in srn mutants. Scale bar = 20 μm. G?J. Reduced protein fucosylation in several neural tissues. Scale bar = 20 μm. K. Protein fucosylation at neuromuscular synapses in WT embryos at 48 hpf, as shown by the colocalization of AAL staining (green) with markers for presynaptic axons and nerve terminals (SV2, red) and postsynaptic AChR clusters (α-bungarotoxin, blue). L?N. Higher magnification of boxed region in K. O. Protein fucosylation is reduced at srn neuromuscular synapses. Scale bar = 20 μm. P?R. Higher magnification of boxed region in O. Synapse area is significantly increased in srn mutants, e.g., at the choice point (compare dashed bracket in Q to solid bracket in M). Scale bar = 20 μm.
|

