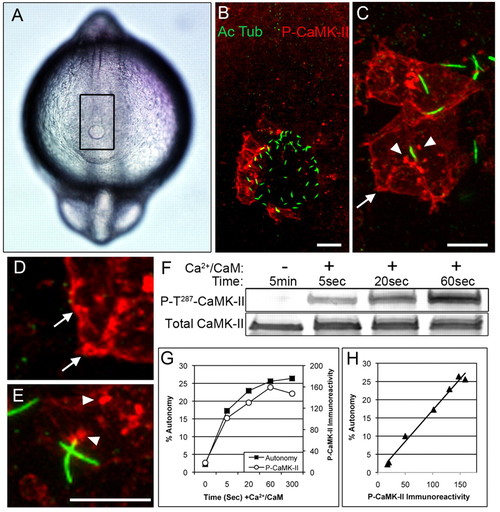
CaMK-II is activated on the left side of Kupffer′s vesicle (KV). (A) Dorsal view of a 12-somite embryo, shows the KV (at the bottom of outlined rectangle) by differential interference contrast microscopy. (B) Confocal immunofluorescence of rectangular region in A using anti-acetylated α-tubulin (green, Alexa 488) to localize cilia and anti-P-T287 CaMK-II (red, Alexa 568) to localize activated CaMK-II in cells on the left side of the KV. (C-E) Higher magnification reveals activated CaMK-II along the cell cortex (arrows) and intracellular clusters (arrowheads), which occasionally colocalize with the base of cilia. Scale bars 10 μm. (F-H) The anti-P-T287 antibody reacts only with activated CaMK-II, as demonstrated by incubating ectopically expressed zebrafish β1K CaMK-II with Ca2+/CaM for the indicated times and then assessing (F) immunoreactivity with anti-P-T287 CaMK-II and an antibody reactive with total CaMK-II. (G) CaMK-II autonomy, measured by peptide assay, and P-T287 immunoreactivity for a representative experiment. (H) When values from four experimental replicates were compiled and plotted against each other, P-T287 CaMK-II immunoreactivity (blot density) was proportional to autonomy.
|

