Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100429-25
- Publication
- Ishida et al., 2010 - Phosphorylation of Junb family proteins by the Jun N-terminal kinase supports tissue regeneration in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
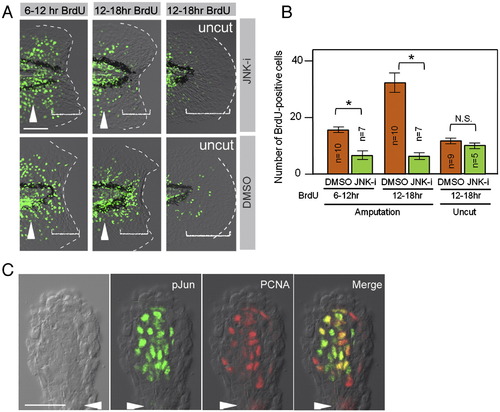
Phosphorylation of Jun proteins by JNK is required for blastema cell proliferation. (A) Decreased regenerative cell proliferation caused by the JNK inhibitor (JNK-i), but not by the vehicle (DMSO). Cell proliferation was detected by BrdU incorporation at 6?12 hpa, 12?18 hpa, and in the uncut finfold. As the regeneration-dependent cell proliferation overlaps with the growth-dependent one that gives rise to the adult-type fin rays (arrowheads), scoring was done in the region within approximately 50 μm from the amputation plane and/or posterior to the notochord end (bracketed areas). Note that the inhibitor treatment did not affect the growth-associated BrdU incorporation. (B) Quantification of regeneration-dependent cell proliferation. The JNK inhibition significantly reduced the regeneration-dependent cell proliferation, but not the growth-associated one seen in the uncut finfold. Error bars depict standard error of the mean (SEM). *P < 0.01. N.S., not significant. (C) Localization of pJun protein in proliferating blastema cells. Whole-mount preparation of adult regenerates at 2 dpa was double-stained with anti-pJun and anti-PCNA antibodies. Most of the PCNA-positive proliferating cells (G1∼S phase of cell cycle) were also pJun positive. Arrowheads indicate the plane of amputation. The scale bar represents 50 μm in (A) and (C). |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Antibody: | |
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Adult |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 340(2), Ishida, T., Nakajima, T., Kudo, A., and Kawakami, A., Phosphorylation of Junb family proteins by the Jun N-terminal kinase supports tissue regeneration in zebrafish, 468-479, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.