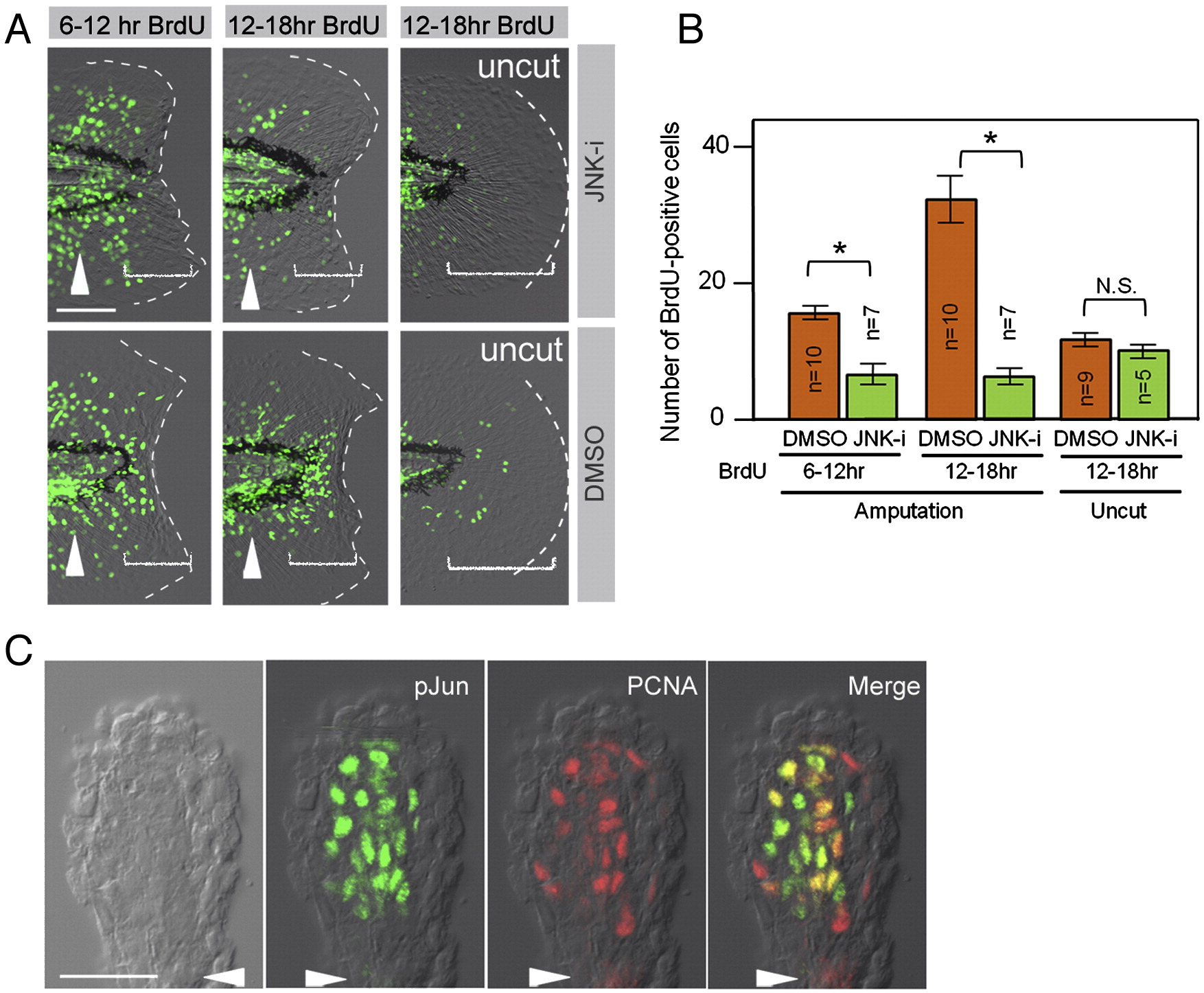
Fig. 4 Phosphorylation of Jun proteins by JNK is required for blastema cell proliferation. (A) Decreased regenerative cell proliferation caused by the JNK inhibitor (JNK-i), but not by the vehicle (DMSO). Cell proliferation was detected by BrdU incorporation at 6?12 hpa, 12?18 hpa, and in the uncut finfold. As the regeneration-dependent cell proliferation overlaps with the growth-dependent one that gives rise to the adult-type fin rays (arrowheads), scoring was done in the region within approximately 50 μm from the amputation plane and/or posterior to the notochord end (bracketed areas). Note that the inhibitor treatment did not affect the growth-associated BrdU incorporation. (B) Quantification of regeneration-dependent cell proliferation. The JNK inhibition significantly reduced the regeneration-dependent cell proliferation, but not the growth-associated one seen in the uncut finfold. Error bars depict standard error of the mean (SEM). *P < 0.01. N.S., not significant. (C) Localization of pJun protein in proliferating blastema cells. Whole-mount preparation of adult regenerates at 2 dpa was double-stained with anti-pJun and anti-PCNA antibodies. Most of the PCNA-positive proliferating cells (G1∼S phase of cell cycle) were also pJun positive. Arrowheads indicate the plane of amputation. The scale bar represents 50 μm in (A) and (C).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 340(2), Ishida, T., Nakajima, T., Kudo, A., and Kawakami, A., Phosphorylation of Junb family proteins by the Jun N-terminal kinase supports tissue regeneration in zebrafish, 468-479, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.