Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100309-36
- Publication
- Gutzman et al., 2010 - Epithelial relaxation mediated by the myosin phosphatase regulator Mypt1 is required for brain ventricle lumen expansion and hindbrain morphogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
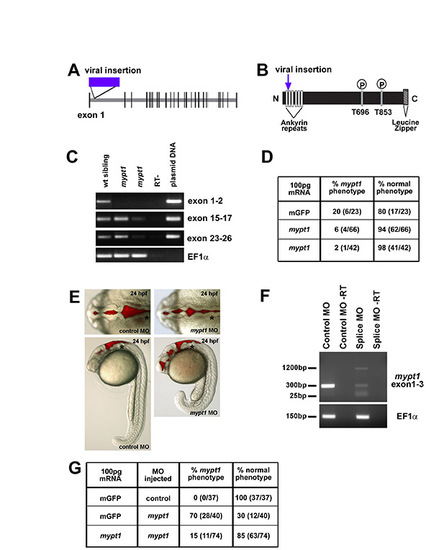
mypt1 gene, protein, mRNA rescue and morpholino phenocopy. (A) In zebrafish, mypt1 consists of 26 exons and a 3322 nt transcript that encodes a 1047 amino acid protein featuring several conserved domains. Model of the mypt1 gene with the location of the viral insertion indicated. (B) Model of the Mypt1 protein showing the viral insertion location in the ankyrin repeat domain. The N-terminus of Mypt1 contains six ankyrin repeats, which have been shown to be important for protein-protein interactions, including the interaction with protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and for myosin phosphatase function. Without proper binding of Mypt1 to PP1, myosin phosphatase is non-functional, regardless of the phosphorylation state of Mypt1. There are two conserved threonine residues at amino acids 696 and 853, which have been demonstrated to be the sites for phosphorylation and inhibition of the myosin phosphatase, and finally a C-terminal leucine zipper motif that is also important for other protein-protein interactions. (C) RT-PCR from single wild-type and mutant embryos over the regions indicated. RT-PCR primers for cDNA analysis of mutant embryos include: exon 1 forward, 5′-AAGGTGAAGTTCGACGATGG-3′ and exon 2 reverse, 5′-GGGGATCCAGCCTTCATTAT-3′; exon 15 forward, 5′-GAACTGTCCTGGGCTCTGAC-3′ and exon 17 reverse, 5′-TCCTGGAGGTCTGTCAATGTC-3′; exon 23 forward, 5′-GGAGAAGGCCACACAGAGAC-3′ and exon 26 reverse, 5′-CGCTCCGTTTTCATCCTTTA-3′. RT-PCR control primers were: EF1α forward, 5′-GATGCACCACGAGTCTCTGA-3′ and EF1α reverse, 5′-TGATGACCTGAGCGTTGAAG-3′. mypt1 appears to be a hypomorphic phenotype as the phenotype can vary in severity from embryo to embryo (data not shown). The transcript was detected, by RT-PCR in different regions of the gene, at different levels in different mutants. (D) mRNA injection and rescue of mypt1 mutants. For mRNA rescue experiments, single-cell embryos were injected with 100 pg mRNA and assayed for phenotype at 24 hpf. Zebrafish mypt1 (NM_001003870) full-length cDNA was obtained by RT-PCR from 24 hpf embryos with the following primers: forward primer (-9 to +10, relative to the start site), 5′-CTCGAGGGGATGAAGATGG-3′ and reverse (+3302 to +3322), 5′-AAACGCAGTGGTTCTGTGTG -3′. The PCR product was sequenced and subcloned into pCS2+ for mRNA expression. mRNA was transcribed using mMessage mMachine (Ambion). (E) Brightfield images with brain ventricle injection demonstrating that the splice site MO phenocopies the mypt1 mutants. (F) RT-PCR analysis of a single embryo to determine the effects of the splice site MO on the mypt1 gene. Primers spanning the splice site target were used, surrounding exon 1-3. RT-PCR primers for cDNA analysis of MO-injected embryos: exon 1 forward, 5′-CGACATCAACTACGCCAATG-3′ and exon 3 reverse, 5′-GGCCTCCTCTTCTGCGATA-3′. The splice site MO decreased the wild-type transcript and introduced two other transcripts. A 1200 bp transcript that included part of intron 2 and caused a frame shift that introduced a stop codon immediately following the MO target site, and a short 30 bp transcript was detected that almost completely excluded exon 2 and introduced a premature stop codon further in the sequence in exon 4. (G) Rescue of the spice site MO-injected embryos with co-injection of mypt1 mRNA. Morphants were rescued by co-injection of 100 pg of mypt1 mRNA at the one-cell stage. |