Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100302-17
- Publication
- Jing et al., 2010 - Temporal and spatial requirements of unplugged/MuSK function during zebrafish neuromuscular development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
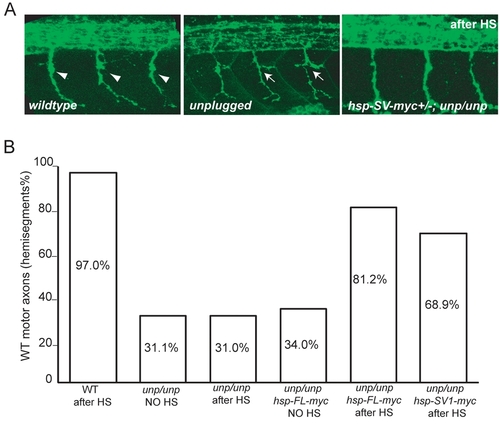
(A) Lateral views of 27-hpf wildtype, unplugged and Tg(hsp70l:unplugged SV1-myc); unpluggedbr307/br307 embryos stained for motor neurons (znp-1). Motor axons in wildtype embryos extend into the ventral myotome after the choice point (arrowheads). unplugged motor axons form lateral branches (arrows), or stall (data now shown) at the choice point. Axonal pathfinding defects were rescued in Tg(hsp70l:unplugged SV1-myc); unpluggedbr307/br307 embryos after the appropriate HS treatment. (B) Quantification of motor axonal phenotypes. Embryos were heat-shocked from the 10-somite stage to 27 hpf. HS treatment did not have obvious effect on motor axon pathfinding in wildtype and unplugged embryos (columns 1?3). In the absence of HS treatment, motor axons remain disrupted in Tg(hsp70l:unplugged FL-myc); unpluggedbr307/br307 (column 4) and Tg(hsp70l:unplugged SV1-myc); unpluggedbr307/br307 (data not shown) embryos. After HS treatment, motor axons were significantly rescued in transgenic embryos (columns 5?6). 20 hemisegments in each embryo were scored. Results are expressed as the average of multiple embryos (n≥20). |