Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090817-47
- Publication
- Curran et al., 2009 - Foxd3 Controls Melanophore Specification in the Zebrafish Neural Crest by Regulation of Mitf
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
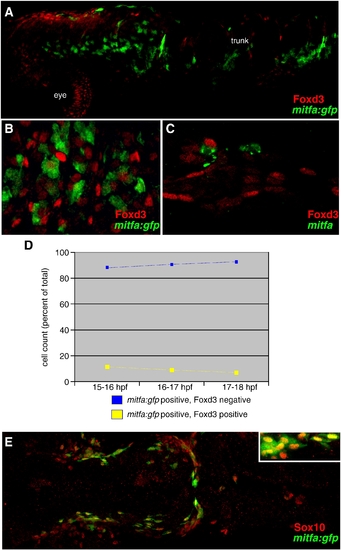
Foxd3 and mitfa expressed in separate populations of neural crest cells. (A) mitfa:gfp positive neural crest cells are mutually exclusive with Foxd3 positive cells, 18 hpf, lateral view, anterior left, 10x. (B) mitfa:gfp up-regulates in Foxd3 negative neural crest cells, 18 hpf, dorsal view, anterior trunk region, 20x. (A, B) Red: Foxd3 Ab. Green: GFP expression in mitfa:gfp transgenic line (C) mitfa up-regulates in Foxd3 negative neural crest cells, 24 hpf lateral view, anterior trunk region. Red: Foxd3 Ab. Green: mitfa mRNA. 20x. (D) Cell counts of mitfa:gfp positive cells derived from 40x confocal images of migratory neural crest cells at three time points: 15?16 hpf, 16?17 hpf and 17?18 hpf. Blue line = percent of total mitfa:gfp positive cells counted which are Foxd3 negative. Yellow line = percent of total mitfa:gfp positive cells counted which are Foxd3 positive. Stage 15?16 hpf, 88% of mitfa:gfp positive cells are Foxd3 negative (583/664); 12% of mitfa:gfp positive cells are Foxd3 positive (81/664). Stage 16?17 hpf, 89% of mitfa:gfp positive cells are Foxd3 negative (497/560); 11% of mitfa:gfp positive cells are Foxd3 positive (63/495). Stage 17?18 hpf, 91% of mitfa:gfp positive cells are Foxd3 negative (448/495); 9% of mitfa:gfp positive cells are Foxd3 positive (47/495). (E) mitfa:gfp positive neural crest cells overlap with Sox10 expression, 91.8% of 250 mitfa:gfp positive cells are Sox10 positive, 20 hpf, dorsal view, anterior left, 10x (inset 20x). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Antibody: | |
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage Range: | 14-19 somites to Prim-5 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 332(2), Curran, K., Raible, D.W., and Lister, J.A., Foxd3 Controls Melanophore Specification in the Zebrafish Neural Crest by Regulation of Mitf, 408-417, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.