Fig. 6
|
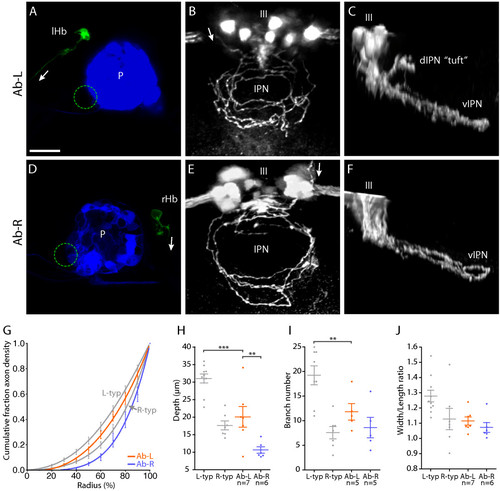
Left and right-sided habenular axons retain distinct morphologies in parapineal-ablated larvae. (a-f) Images from brains of 4 dpf Tg(flh:eGFP); Tg(foxD3:GFP) transgenic larvae in which parapineal ablation was performed at 24–28 hpf and single neurons in the L or R habenula were labeled by focal electroporation at 3 dpf. (a, d) Confocal z-projections of the dorsal diencepahlon confirming successful ablation of the parapineal (indicated by dotted circles) and labeling of single L (a) or R (d) habenular (Hb) projection neurons. 'P' indicates pineal. (b, c) Dorsal (b) and lateral (c) views of flattened axonal arbors elaborated by single L-sided neurons in the vIPN after parapineal ablation. Axon branches frequently extend towards the center of the vIPN in these arbors. Some L-sided axons extend collateral branches into the anterior dIPN that terminate with a unique tuft morphology (tuft in (c)). The oculomotor nucleus (III), which lies just anterior to the IPN, expresses GFP in these transgenic larvae and allows the DV position of the arbors to be determined. (e, f) Dorsal (e) and lateral (f) views of arbors formed by single R-sided neurons after parapineal ablation. These arbors appear as a more exaggerated form of the R-typical morphology. Axon branches are strongly localized to the perimeter of the arbor and extend over a very limited DV depth. Arrows indicate the direction of projection of habenular axons. Scale bar in (a): 20 μm. (g) Radial distribution of axon density for six Ab-L and five Ab-R arbors. Distribution profiles for L-typical (L-typ) and R-typical (R-typ) arbors are shown in grey. (h) Both Ab-L and Ab-R arbors extend over a limited DV depth, similar to R-typical arbors; however, Ab-R arbors are significantly flatter than Ab-L arbors. (i) Ab-L arbors have a reduced number of branch points compared to L-typical arbors. (j) The width/length ratio of Ab-L and Ab-R arbors are similar to those of R-typical arbors. In (g-j) the L-typical and R-typical data, shown in grey, are the same as presented in Figure 3. Horizontal lines indicate mean values and error bars show standard error of the mean. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. |