Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-071005-45
- Publication
- Walshe et al., 2003 - Fgf signalling is required for formation of cartilage in the head
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
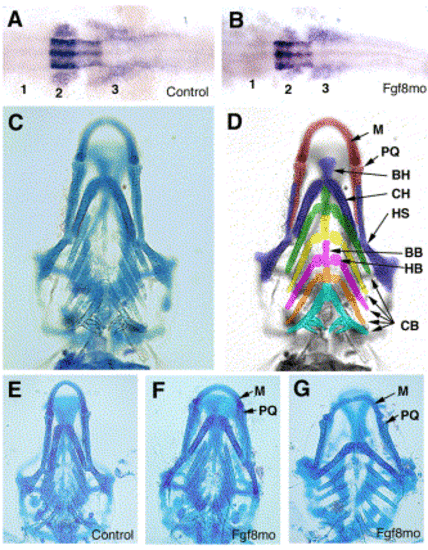
Effects of inhibition of Fgf8 on Hoxa2 expression and pharyngeal cartilage. (A, B) Hoxa2 expression in 18-hpf embryos following injection of control morpholino (A) or Fgf8mo (B). Transcripts are detected in the hindbrain and in the second (2) and third (3) neural crest streams that will populate the second (hyoid) pharyngeal arch and posterior arches, respectively, but are not detected in cells in the position of the first (1) stream. (C) Ventral view of a wild type embryo stained for cartilage at 5 days of development. (D) The same embryo as in (C) but with the skeletal derivatives of each arch differentiated by colour and individual elements labelled: arch 1, red; arch 2, blue; arch 3, green; arch 4, yellow; arch 5, pink; arch 6, orange; and arch 7, turquoise. (E–G) Ventral views of embryos injected with the control morpholino (E) or Fgf8mo (F, G) and allowed to develop to 5 dpf, then stained for cartilage. The eyes have been removed from (C, E–F) to improve visualization of the skeleton. Abreviations: M, Meckel's cartilage: PQ, palatoquadrate; BH, basihyal; CH, ceratohyal; HS, hyosymplectic; BB, basibranchial; HB, hypobranchial; CB, ceratobranchials. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 264(2), Walshe, J. and Mason, I., Fgf signalling is required for formation of cartilage in the head, 522-536, Copyright (2003) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.