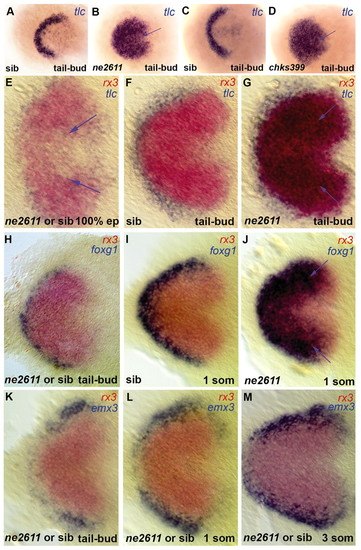
Rx3 controls early patterning of the presumptive anterior forebrain. Expression of the markers indicated (color coded) in ckhne2611 (B,G,J), ckhs399 (D) or their wild-type siblings (A,C,F,I); E,H,K-M are non-genotyped embryos from crosses between ckhne2611/+ heterozygotes. All views are dorsal anterior left in whole embryos (A-D) or flat mounts (E-M). (A-D) tlc expression identifies the presumptive telencephalon at tail-bud stage and is massively expanded in both ckhne2611 (B) and ckhs399 (D) mutants compared with their wild-type siblings (A,C). (E-G) No difference in tlc expression is observed between wild-type and mutant embryos at 100% epiboly, when tlc expression is downregulated from the presumptive eye and hypothalamus fields, labeled by rx3 (see the few remaining tlc-positive cells in the rx3-positive domain at 100% epiboly; arrows in E, absent in F). At tail-bud stage the ectopic tlc expression overlaps the rx3 domain (G, blue arrows). (H-J) Expansion of foxg1 across the eye field is absent at tail-bud stage (H) but is visible at the one-somite stage (J, blue arrows). (K-M) The relative expression of emx3 and rx3 are not noticeably affected in mutants before the 3-somite stage.
|

